The decade of fog computing has begun. Ushered in by a specific set of high-velocity digital business problems and growth opportunities, fog computing is rapidly gaining traction.
For those involved in the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G, artificial intelligence and virtual reality, fog computing is more than an interesting approach: It’s a necessary one.
Why? In today’s digital world, you can’t run everything in the cloud. There are latency, mobility, geographic, network bandwidth, reliability, security and privacy challenges. Nor can you run everything at the edge with intelligent endpoints, due to energy, space, capacity, environmental, reliability, modularity, and security challenges, says Lynne Canavan, executive director, OpenFog Consortium.
Fog computing addresses these gaps by bridging the continuum from cloud to things. It distributes compute, communication, control, storage and decision making closer to where the data is originated, enabling dramatically faster processing time and lowering network costs. Fog is an extension of the traditional cloud-based computing model where implementations of the architecture can reside in multiple layers of a network’s topology. By adding layers of fog nodes, applications can be partitioned to run at the optimal network level.
In particular, fog computing supports time-critical applications that require sub-millisecond reaction time. Autonomous vehicles, emergency responsiveness, drones and virtual reality are among the dozens of applications that require rapid latency. For example, a drone can travel at 100 miles per hour, or roughly 147 feet per second.
During its journey, it requires continuous software updates, produces massive amounts of data that require computation and communication. If you consider that the best cloud round trip latency is around 80 milliseconds, the drone would fly about 12 feet between cloud messages. Fog nodes can reduce the latency to such a degree that a drone will only travel two inches before the next update is delivered.
Fog computing also supports data-intensive, remote operations. In oil and gas exploration, real-time subsurface imaging and monitoring reduces the drilling of exploratory wells, saving money and minimising environmental damage. Thousands of seismic sensors generate the high-resolution imaging required to discover risks and opportunities.
Fog computing manages the energy, bandwidth and computing needed for timely risk and opportunity analysis in this geographically-challenged, disruption-prone and data-intensive process. Instead of collecting data in the cloud for post-processing, fog nodes form mesh networks to stream data processing tasks and communicate with each other to compute the subsurface image in the network.
The fog computing algorithm is resilient to network disruption and adapts to energy and bandwidth changes. To work, fog computing must enable rapid, trusted and secure transmissions.
This requires an open, interoperable architecture that will ultimately enable end users to choose interoperable solutions from a diverse, vibrant supplier ecosystem. Creating the open architecture, and testing it via fog computing use cases and testbeds, is the work of the OpenFog Consortium.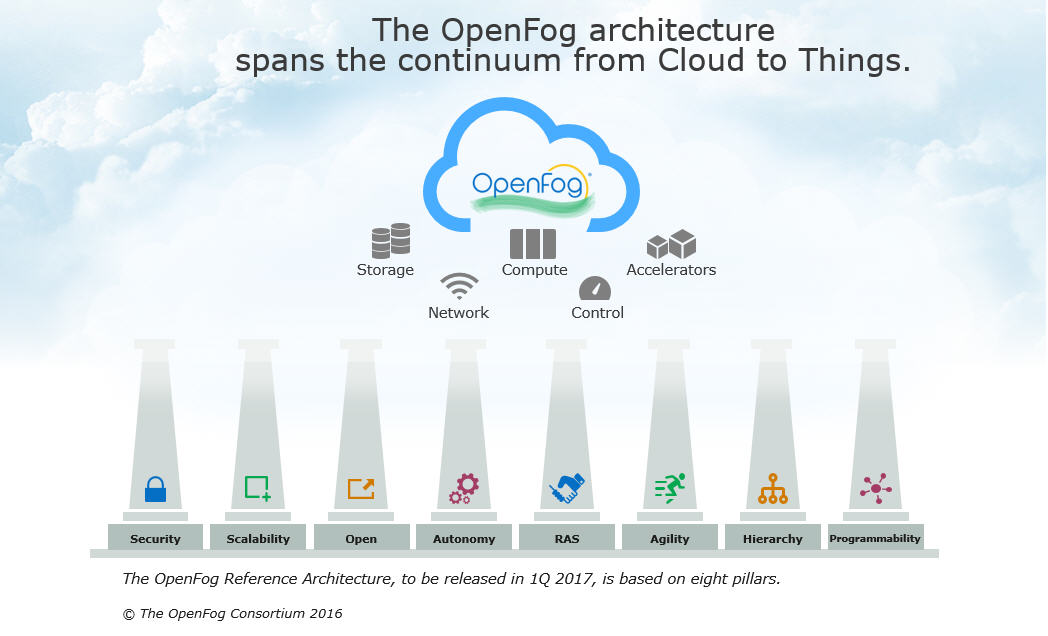
The OpenFog Consortium was founded in November 2015 by ARM, Cisco, Dell, Intel, Microsoft and Princeton University, based on the shared vision that an open fog computing architecture is necessary in today’s increasingly connected world.
Our mission is to drive industry and academic leadership in fog computing architecture, testbed development, and a variety of interoperability and composability deliverables that seamlessly leverage cloud and edge architectures to enable end-to-end scenarios. Through an open membership ecosystem of industry, end users, universities and research organisations, OpenFog is collectively applying a broad coalition of knowledge to the technical and market challenges ahead.
Today, 51 member organisations from 14 countries are collectively working on the OpenFog reference architecture, to be released in early 2017. This framework is based on eight foundational pillars: Security, scalability, openness, autonomy, RAS (reliability, availability and serviceability), agility, hierarchy, and programmability.
From the silicon layer through to the operating system, OpenFog members are defining and testing functional and component level interoperability for fog-to-fog communication, by applying the architecture to specific use cases. Standards development organisations will then use this architecture to create the specific standards.
Driving business growth through fog-enabled applications is the ultimate goal of our work. The OpenFog architecture is the underlying framework to build and test new concepts and products in real-world use cases and testbeds. Smarter cities, drone-enabled supply chains, remote energy extraction and exploration, smart traffic, video surveillance, virtual reality, environmental conservation and emergency response are just a sample of the emerging use cases that are enabled and improved through fog computing.
The future is looking very foggy indeed.
This author of this blog is Lynne Canavan, executive director, OpenFog Consortium
Comment on this article below or via Twitter: @IoTNow_ OR @jcIoTnow










