Technology market researchers forecast that by 2020 connected devices and things will exceed 20 billion. The data volume generated by this mass will dwarf the current big data produced primarily by social networks.
Therefore, organisations need to ensure that future data pipelines are powerful enough to handle and process this predicted increase in telemetry data, yet stay flexible enough to react to changing business needs. To this end, there are a number of important considerations…
Flexible architecture
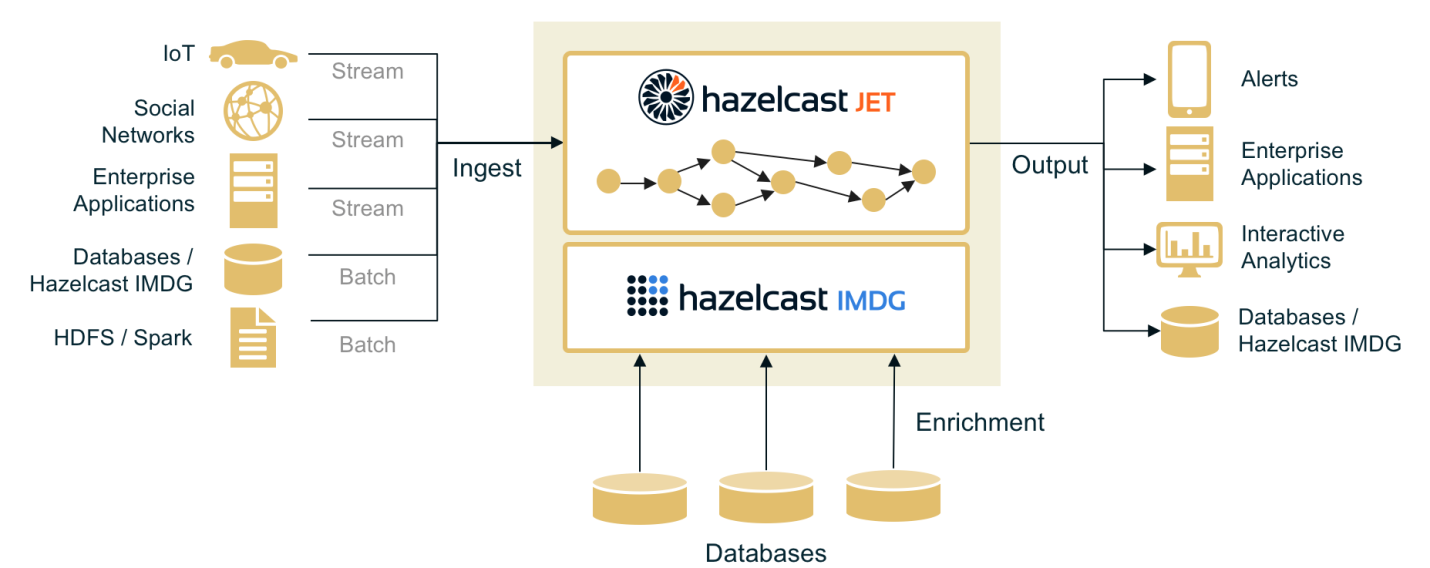
The main goal of device-ready architecture is to provide a new layer which binds traditional enterprise systems with devices and positions data as a first-class citizen, says Vladimir Schreiner, Product manager at Hazelcast.
Using this architecture, data from devices comes in the form of a continuous stream of individual events. Events hold the telemetry information (measurements, status updates, alerts) and the data pipeline transports those events, ensures authorisation and filtering, processes the events and provides processed data to enterprise systems.

Volume in real time
One of the key challenges of event stream pipelines is to handle speed at scale. Solutions must be capable of continuously processing big data volumes, while ensuring low end-to-end latency.
Data flowing in Internet of Things (IoT) systems are generally latency-sensitive, meaning it loses value with time meaning it needs to be processed as soon as possible. Data analysts cannot report serious problems in hours, or even in minutes. Alerts needs to be immediate.
To achieve this near real-time operation, streaming data must be processed on-the-fly (prior to storage). On the stream ingestion level, this mostly equates to:
- Device and event authorisation and filtering to ensure security
- Device status updates
- Message format translation/conversion/normalisation
Pre-processed events are routed for downstream processing which means the stream processing unit must perform on-the-fly analysis and anomaly detection, which typically means:
- Search for complex events to detect anomalies and trigger alerts
- Compute stats
- Match streaming data against machine-trained model
To achieve all of this, a powerful solution is necessary. The stream processing engine must be able to handle large loads with flow peaks (the cluster has to be elastic to scale with current load) and guarantee low-latency.
Fast data access and latency
It is not just speed and latency of a processing unit which matters. Low latency must be provided end-to-end i.e. starting from the event emitting by the device to the response. The messaging and storage involved in the pipeline may become a bottleneck if not designed properly.
Therefore, when storage and processing meet, the former must be engineered carefully and have the following functionality:
- New datasets entering the processing, such as device registry or enrichment data store
- Operational storage for publishing and the updating of results
- Messaging tool for passing data between units of data pipeline
To achieve all of this, an In-Memory Data Grid (IMDG) is a good fit as it is inherently quick and solves storage issues by forming storage clusters, in addition it can transmit reactive access patterns to notify analysts when values change. Therefore, it can be used as a cache for big datasets during processing, while forming in-memory data lakes for frequently used data.
Saving bandwidth to reduce costs
Another idea is to reduce the data flow between the field and data centre via edge processing i.e. processing close to the data source. Data streams can be aggregated and filtered prior to being sent to the data centre, thus reducing transmission costs. When you consider data streams of gigabytes per second, the gained flow reduction would be significant. Importantly, stream processing technology must be lightweight.
Introducing Hazelcast Jet – a potential solution
Simple to deploy, Hazelcast Jet is an in-memory streaming and fast batch processing engine and a building block for IoT data pipelines. It is used to process big data volumes with low latency. Flexible enough to conduct edge processing, server-side stream processing, and subsequent data-at-rest batch processing, it comes integrated with a scalable, in-memory storage layer – Hazelcast IMDG.
Hazelcast Jet is appropriate for applications that require a near real-time experience such as sensor updates in IoT architectures (house thermostats, lighting systems), in-store e-commerce systems and social media platforms.
The author of this blog is Vladimir Schreiner, Product manager at Hazelcast
Comment on this article below or via Twitter: @IoTNow OR @jcIoTnow










