In this article, Robin Duke-Woolley, Analyst and CEO of Beecham Research, shares his latest insights from the Energy sector on the key issues facing the market and how IoT is addressing them.
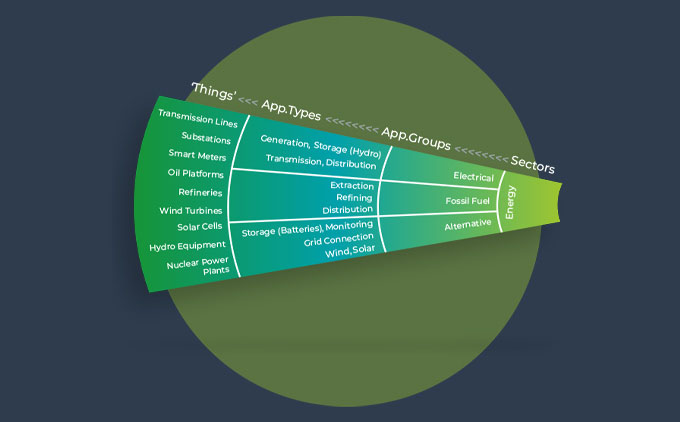
Energy generation and distribution includes electricity, smart grid and renewables, oil and gas exploration and production.
1. Key issues in the sector:
There are two main challenges facing the energy sector today.
- Assuring sustainable supplies of energy for the coming decades
- Mitigating the effects of climate change.
- Sustainability of energy resources
Rising demand is inevitable as populations grow and natural resources (fossil fuels) are no longer inexhaustible. Governments worldwide recognise the need to reduce fossil fuel consumption and consequent pollution; they stipulate that industry must move towards net zero carbon operations, replacing fossil fuels with renewables(wind, solar, nuclear).
As these renewable sources are coming into the mix, these are changing and complicating the pattern of electricity generation and usage. Incorporating renewables will go some way towards securing long term supplies, but these are by nature intermittent and decentralised. The ongoing replacement of petrol cars with electric vehicles will put additional demands on power supplies and bring about new patterns of electricity usage.
On the consumption side, Industry 4.0 is increasingly reliant on sophisticated control systems, which rely on uninterruptible and predictable power supplies. In addition, the escalating number of devices in IoT networks and their power requirements will also increase the pressure. One of the biggest challenges with implementing the Industrial Internet of Things is managing data transmissions between many IIoT devices in remote sites.
Oil and Gas production also faces increasing demand as resources dwindle. This is being met through discovering and exploiting harder to reach reserves and developing new extraction techniques; this is concomitant with ever stricter health and safety regulations for workers.
- Mitigating the effects of climate change
The world is seeing more and stronger storms, wildfires, outages and flooding, all affecting energy generation and distribution operations. A recently revised report (February 2022) from the IPCC (International Panel on Climate Change) states that climate change is already going beyond the ability of many societies to cope.
2. How IoT is addressing these issues
The power infrastructure of tomorrow needs smart, connected energy networks comprising generation, transmission and distribution operations.
The Internet of Things enables organisations to capture more granular data and perform sophisticated analytics, allowing the optimisation of resource usage through measurement. Sensor networks transmit data to the Cloud or the Edge in real time or near real time, where it is analysed to gain insights and better understanding of their workings, as well as identify areas for improving efficiency.
All this goes hand in hand with the ongoing digitisation of the energy industries. Digitisation is the gathering and transferring of information from analogue to a shareable digital form. Capturing asset, meter, and customer data digitally helps the modern supplier identify areas where automation can enhance productivity and reduce uncertainty.
Some of the many areas where IoT is assisting with this include the following:
- Analytics for demand forecasting – forecastingof energy usage affords a real-time view of energy as it is generated and consumed. Suppliers are particularly under pressure to increase efficiency through grid optimisation, increase the supply of renewable and distributed power generation, and manage risk within volatile energy commodities markets and changing usage patterns. Forecasting applications utilise IoT data as well as historical and environmental data to reduce uncertainty for operators.
- Asset monitoring – Industrialasset monitoring tracks the status of equipment and ensures that it operates smoothly. Sensors register a range of signals including vibration, temperature, motor current fluctuations etc. making possible remote inspection across wide areas.
- Automated vehicle tracking and guidance – forexample for oil and gas and mining at remote sites.
- Connectivity:
- 5G in power networks. Much has been written on this topic. As one example, the Wive Project in Finland aims to demonstrate that requirements for reliability, latency, data rates and security for industry segments, including smart grids, can be fulfilled with future 5G networks.
- LPWAN: Secure and cost-effective connectivity is a prerequisite for remote data collection. Connectivity, whether it be fixed, power line comms or wireless, needs to be extra reliable in emergency situations and the failover is often over cellular networks. Low-Power Wide Area Networking (LPWAN) is finding favour due to its low power, low data rates, and support over long distances (km).
- The cost and burden of setting up a landline connection for each site may be uneconomic. Cellular offers a reliable solution to manage remote assets, for Demand Response for example.
- Private cellular networks. Private cellular networks (PCNs) small cells are suitable for sites of centralised energy generation. Large cell PCNs are suitable for larger networks including renewable sources, the Grid, substations and power Transmission and Distribution networks.
- Customer engagement – theability for customers to switch energy suppliers makes it imperative for suppliers to measure and gauge quality of service (QoS). IoT data-based applications can improve customer service and satisfaction by highlighting areas for improvement.
- Demand Response – regulatorychanges to the energy industry allow operators to maintain grid reliability by reducing system demand during peak periods. This depends upon being able to measure demand and usage.
- Digital twins can help manage increasingly complex assets and anticipate problems before they happen by creating an accurate virtual replica of physical objects. Asset data is leveraged to simulate asset performance under varying conditions, based on known risks and usage information.
- Drones – inspectindustrial installations from the air including power generation plants, oil and gas platforms, power lines, oil and gas pipelines.
- Edge computing, in which data is processed locally to its generation, provides near real time processing of data for fast response and reduces the need to send all data to the cloud. It is being adopted by energy companies whose assets are widely distributed.
- Lone worker protection – employsa wireless device fitted with GPS that tracks workers in hazardous, isolated work environments, enforcing stricter health and safety adherence. Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality are tools to help workers visualise situations at the location where they are working. They are particularly useful in offshore platforms.
- Predictive maintenance – analysingdata from instrumented machinery to anticipate when it might fail, avoiding downtime.
- Security and cybersecurity – asecure, reliable and resilient wireless communication network enables suppliers to deliver many new services to commercial and domestic customers. They need to be able to connect to customers’ smart meters, Nest Thermostats, air conditioners and all manner of industrial machinery.
- Smart metering – measuring energy usage remotely and in near real time, affording visibility into the dynamics of the industry, supply and demand. This enables more efficient, demand-based electricity generation and distribution.
- Usage based billing and fraud detection – industryresearch indicates that utilities lose up to 5 percent of their revenue annually to non-technical loss, including energy theft and fraud.
3. How the IoT World Map can assist
IoT solutions have several different elements and can be complex. This complexity will also increase with more use of real time processing, the introduction of private networking and the rollout of 5G. Each of these offers major benefits in this sector but assistance from IoT solution experts with specific knowledge of the energy sector is increasingly needed. This presents a difficulty for IoT buyers, who typically have to identify which suppliers have specific knowledge of their application areas.
The IoT World Map is arranged so that those requiring IoT solutions can access the map knowing only the applications they need support for in their own sector. IoT suppliers who have direct energy sector experience and can assist specifically in energy solutions can be readily identified and contacted.
The aim of this is to assist IoT buyers to proceed more quickly to solution design and implementation.
Robin Duke-Woolley
Beecham Research