This insight explores how the Internet of Things can address challenges in the construction industry and in building automation.
Both segments face major challenges in adapting to a post Covid era, responding to new legislation to move towards zero carbon emissions, and assuring resilience from the effects of climate change.
1. Key Issues in the Sector
Construction
- Cutting energy consumption
According to the International Energy Agency, buildings were responsible for 28 percent of global energy-related CO2 emissions in 2019. Since 2016, increased demand for building services – electricity for cooling, appliances and connected devices – has outpaced energy efficiency and decarbonisation efforts; this has resulted in a net growth in emissions from buildings. Now achieving net-zero buildings by 2050 to combat climate change has become a global mandate. The corporate sector has a central role in reducing total emissions from their businesses in line with validated, science-based targets.
- Building resilient infrastructure
The UN’s Sustainable Development Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked global goals designed to be a “blueprint to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all”. Goal no 9 is to build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialisation and foster innovation. Resilient infrastructure would minimise the future effects of climate change. Demand for sustainable workplace space is growing, with occupiers driving towards net zero targets, investors anticipating increasing regulation and enterprises espousing Environmental Social and Corporate Governance.
- Digitising the industry
Construction jobs have mainly necessitated people on site. The pandemic has widened the adoption of digital tools, including those that enable remote work. Construction projects typically entail complex partnerships composed of stakeholders from different disciplines: as well as ICT vendors, they include governments, investors, regulators, local authorities, landowners and industry groupings. All of these must have access to up to date and accurate information about projects in progress and their participants.
With the pandemic forcing companies to adopt remote working practices, the construction industry is looking for ways to keep fewer people on site; hence the situation will likely lead to a more rapid adoption of digital tools such as Artificial Intelligence and automation.
Buildings Automation
The principal challenges here are
- Reducing energy consumption; to comply with climate goals, operations must also reduce waste and increase efficiencies.
- Assuring health and safety; as businesses return to commercial offices post Covid, they must return to greatly improved and safe working conditions.
- Buildings must comply with stringent government regulations to build sustainable and resilient structures. Achieving net zero by 2050 may also require a major retrofit to existing housing stock. Meanwhile new materials are being sought for carbon friendly construction, while the optimal use of existing materials is encouraged.
2. How IoT is addressing these challenges
The IoT can help in ensuring that buildings are not only safe to construct, but also safe for those who live and work in them. A range of IoT solutions exist to address these goals, solutions which utilise sensor connected networks together with analytical software.
Construction
- Design phase: safety should be built in during the design phase. Digital Twins are a digital replica of a physical object, but with live data advising on how the asset runs and operates. The technique can improve the understanding of the resilience of buildings to climate change, capture the impact of any changes and how they can prevent accidents from happening.
Keeping track of all participants through tools such as Building Information Modelling. Traditional drafting tools can, if digitised, lead to different models that automatically support contracting and reporting, in addition to checking specifications of components before they get ordered and built in.
- Build phase: Buildings Information Modelling (BIM) is a toolset used to model all the data associated with the building. This includes geographic data, urban and environmental data, and ensures the coherence of the data and makes it available to all participants in the project. BIM can reduce the environmental footprint of the project, reduce delays and improve quality. It also ensures that new buildings comply with health and safety and other legislation.
- Monitoring existing or new structures for cracks and structural flaws through embedded sensors. For example, concrete plays a pivotal role in all major construction initiatives; the stakes are high, and there is almost no margin of error, making the close monitoring of concrete curing and maturity vitally important.
- Predictive maintenance of various machine tool types and toolsets ensures that breakdowns can be anticipated ahead of time and avoided.
- Smart tools and tool tracking, possibly part of a larger solution integrated with construction management and project planning
- Security: Access control at building sites via video surveillance and peripheral security monitoring to detect unauthorised entry.
Dangerous building sites keep Lone Workers safe through alarmed wearables.
Building Automation
IoT offers analytical tools to be able create healthier workspaces in the built environment. Examples include:
- Structural health monitoring and tracking of factors including Vibration, Strain, Stress, Dampness etc. For example, it is believed that the fatal collapse of a condominium in Miami, FL in 2021 could have been averted with timely monitoring of structural faults.
- Predictive maintenance of machinery including elevators, escalators, anticipating breakdowns before they occur
- Facilities management operations monitoring through systems to manage the temperature, humidity and lighting to make the most efficient use of resources
- Asset tracking and management including movable assets, such as furniture and equipment
- Water monitoring – leaks detection
- Occupancy detection and analytics for workspace usage optimisation; for example monitoring room occupancy and occupant behaviour during the course of the day; keeping a healthy distance between workers
- Smart window and lighting control, controlling daylight level shading through blinds control
- HVAC (Heating ventilation and air conditioning), to protect from Coronavirus and other airborne bugs that might be blown around on the ventilation system; detecting Carbon Monoxide, Carbon Dioxide, particulates, allergens, etc.
- Site security and access control, video cameras
- Automated fire detection and extinguishing systems, and wayfinding to assist occupants in case of evacuation.
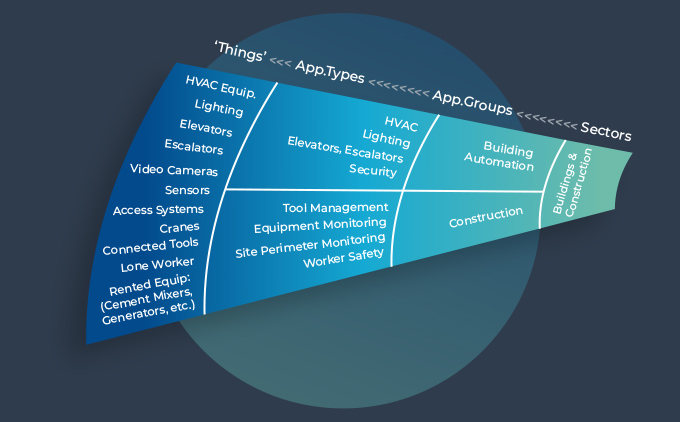
3. How the IoT World Map can assist
IoT solutions have several different elements and can be complex. This complexity will also increase with more use of real time processing, the introduction of private networking and the rollout of 5G. Each of these offers major benefits in this sector but assistance from IoT solution experts with specific knowledge of the Buildings & Construction sector is increasingly needed. This presents a difficulty for IoT buyers, who typically have to identify which suppliers have specific knowledge of their application areas.
The IoT World Map is arranged so that those requiring IoT solutions can access the map knowing only the applications they need support for in their own sector. IoT suppliers who have direct Buildings & Construction sector experience and can assist specifically in such solutions can be readily identified and contacted.
The aim of this is to assist IoT buyers to proceed more quickly to solution design and implementation.
Robin Duke-Woolley
Beecham Research