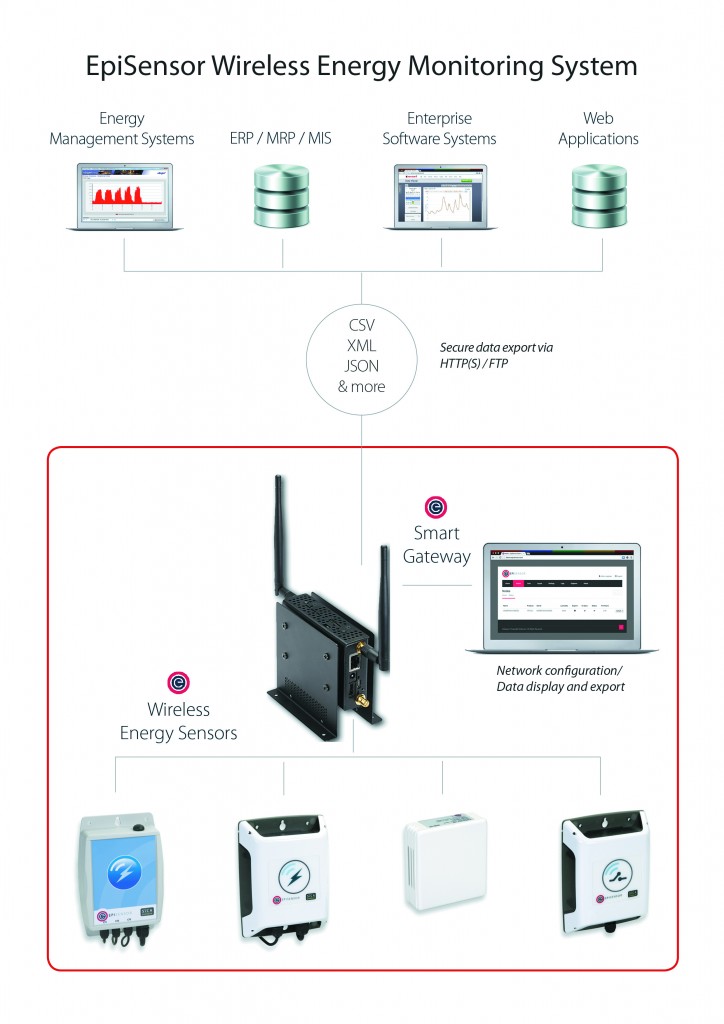
(European Utility Week, Amsterdam preview) — To identify energy saving opportunities, companies first need to have a detailed view of their energy consumption within a facility or group of facilities. EpiSensor provides a wireless energy monitoring system for this task. The system includes ZigBee connected sensors and an enterprise-class energy monitoring gateway, which runs on Kontron’s M2M smart services platform.
The EpiSensor system is capable of pushing data to a broad variety of energy dashboards and enterprise software systems. Customers benefit from a set-up that is said to be virtually IT infrastructure-independent and does not need to be hosted on the customer’s own servers.
As a first step towards reducing energy usage and costs, companies need to install a plant-wide measurement system. EpiSensor, one of the leading companies in this sector, has been lowering energy costs for international Fortune 500 customers in energy-hungry industries since 2007. Customer references for the Ireland-based company include Smurfit Kappa Group which produces paper-based packaging, the food processor Foyle Food Group, DePuy/Johnson & Johnson which manufactures medical devices, and Mylan which develops pharmaceutical products. Citibank uses EpiSensor’s wireless energy monitoring system to optimise facility management of a large landmark building with 2.000 occupants.
The smart data logging sensors
To enable flexible and fast installation, EpiSensor’s energy monitoring system utilises advanced self-healing mesh networking technology to collect data from wireless nodes. Multiple waterproof sensors placed throughout the facilities log time-stamped data at the sensor level, which serves as a redundant back-up in case of any network communication issues. The sensors use AES 128-bit encrypted communication over a ZigBee wireless network (IEEE 802.15.4). EpiSensor wireless products have a range of up to 100 meters and the network can scale to several hundred distributed nodes within a single wireless network.
The new open and flexible gateway
EpiSensor’s gateway has two main functions: to manage the wireless sensor network and to export high quality energy usage data to third party systems for display, archiving and analysis.
For management and monitoring, EpiSensor’s gateway provides access to a buffer of live data as well as to the sensor settings through a built-in web server. The sensor data can be delivered to a variety of energy dashboards and enterprise class software systems such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) or MIS (Management Information Systems) as well as technical management systems such as EMS (energy management systems). Data can be sent in a range of formats, such as CSV, XML, and JSON, over various protocols including FTP and HTTPS.
Fully compatible with all modern smartphones, tablet computers and desktop web browsers, the intuitive interface provides technical information that is typically not exported, such as voltage, peak current, or battery level. A data view module supports the visualisation on public displays to raise awareness of energy usage.
No specialist training is required to install and administer the EpiSensor system. EpiSensor’s gateway can connect to the Internet or Local Area Network via Ethernet, Wi-Fi or a cellular modem.
Improvements to previous gateways
EpiSensor’s new gateway platform has been re-designed from the ground up to be more scalable, reliable and easier to use. Previously, the company’s wireless energy monitoring system was managed via PC-based software with data storage and export handled on a server running EpiSensor software. All of this functionality has been condensed into the gateway, which reportedly makes the system easier to deploy in complex IT environments by removing the requirement for a server component, and makes it easier to install by providing access to all of the system’s features from the user-friendly web interface. On the new platform, EpiSensor also has expanded the original feature set to include more data export options, better data visualisation and more advanced network management functionality.
M2M smart services management box
With a need to incorporate significant software-based functionality into its smart energy monitoring gateway, EpiSensor chose an embedded OS-based M2M smart service management box that is powerful, open and programmable. After deciding on an Intel® platform, EpiSensor opted for Kontron, a preferred Intel® platform provider that offers ‘one stop’ embedded computing competence as well as M2M know-how.
Cellular connectivity
The professional grade M2M platform from Kontron is based on SFF Intel® Atom™ processor technology and delivers the connection into the cloud using the 3G/2G cellular connection as a standard or fall-back functionality for a wired telecommunication connection. This integrated connection is application-ready in a versatile embedded computing box that includes all the required drivers and protocols plus highly flexible configuration options in terms of applications and operating systems.
Pre-qualified M2M platform
Beside this flexibility, the platform wins over research and development (R&D) engineers with its pre-qualified set-up for mobile network operators. The system offers pre-integrated cloud services from third party vendors, has PTCRB certification and is approved by global carriers for use in cellular networks. This saves R&D time as well as costs, for companies such as EpiSensor, as it streamlines the process of carrier approval and their own certifications before a large scale field deployment takes place. For use as part of a smart grid, it also can be manufactured accordingly.

Flexible device interfaces
Locally the system provides direct access either via Ethernet or WLAN (Wi-Fi) to the EpiSensor energy monitoring platform. For integration of additional sensors and other terminal devices, the Kontron M2M Smart Services Developer Kit carries a range of interface options including 802.11a/b/g/n WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) and 802.15.4 WPAN (Wireless Personal Area Network) as well as a Mini PCI Express slot for customer-specific extensions.
Even the integration of a surveillance system is possible with the optional extension of a smart video and audio module. Additionally, custom configurations are available, if required by the OEM. With its modular approach and custom design options, the M2M developer kit enables OEMs and smart services developers as well as independent software suppliers (ISVs) to reduce development costs and risks, thus ensuring a rapid introduction to the market.