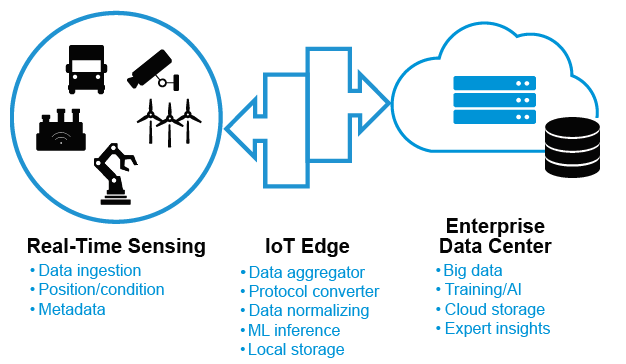
IIoT Strategies need to Evolve
The hype of billions of devices connected through the internet sounds promising. A connected, AI-supported smart factory will help reduce costs and increase operational efficiency. Sensor-based health care solutions and a highly personalized consumer experience will improve our quality of life. Driverless trucks would transform the logistics industry and support our need for faster, on-time deliveries.
But imagine aggregating zettabytes of data from these endpoints and pushing that intelligent information through a constrained network infrastructure. Or, the cost of storing and managing this information in cloud platforms and datacenters where they charge per megabyte of raw data. Moreover, industrial systems need to react within highly accurate, millisecond control loops and fixed latency requirements, so sending data to the cloud will just not allow for industrial real-time command and control.
Many companies that have developed IIoT strategies are finding it difficult to move passed their proof-of-concept to a scalable, commissionable industrial system unless they address these challenges and therefore need to consider how their IIoT architectures must evolve.
The Intelligent Edge
The IIoT architecture will need an updated approach that brings compute and analytics closer to the source of data, not just to address the cost of sending data to the cloud, but also to be able to react to real-time events. Network systems that were once used as data aggregators and protocol translators are being replaced or supplemented with more intelligent solutions with on-premise compute and storage to bridge between the real-time systems and the IT domain.
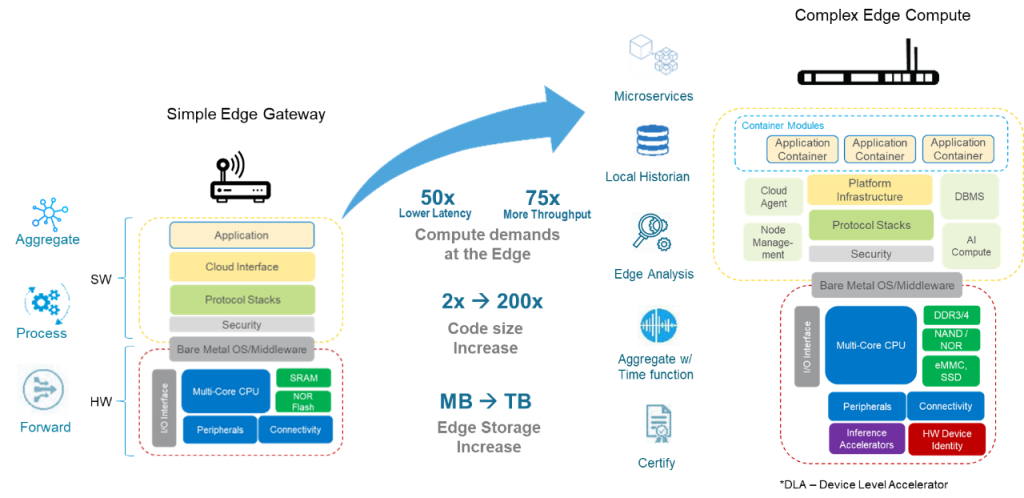
The intelligent edge solution must be able to accommodate Edge-purposed software platforms that are not just an extension of cloud functions, but also allows for a disaggregation of functions and a seamless integration between the endpoint and the enterprise cloud. Simple gateways that were designed as a single OS software architecture will be replaced with edge compute systems with multiple virtual functions, or containers that support disparate services.
Edge Solutions and the Role of Memory
There will be a wide range of edge solutions that will vary based on the compute performance requirements as well as how the cloud/enterprise will be able to integrate to it. The embedded resources within these solutions will vary as code size and storage requirement grows.
The use of hobbyist gateways will evolve to more sophisticated architectures that pack more compute and storage for on-site processing of information, and will need:
- Ability to support multi-sensor data aggregation and connectivity in real-time
- Multicore processor systems with hardware AI accelerators that support deep learning inference and higher compute requirements
- Embedded local storage for on-premise data management
- New software middleware and APIs to support network virtualization and containers for microservices
There are a growing number of chipsets and ASICs that embed AI accelerators but their compute performance is limited by the memory access operation. Edge compute systems that need to support machine learning inference up to GPU-level compute performance, will require high performance dynamic RAM (DRAM) solutions, not just in terms of megatransfers per second (MT/s) throughput but incorporate more efficient memory bank usage and therefore improve overall effective bandwidth. For example, Micron compared our DDR4 at an equivalent data rate of 3200 MT/s vs our latest DDR5 system-level simulation and indicates an approximate performance increase of 1.36x effective bandwidth. At a higher data rate, DDR5-4800 will have an approximate performance increase of 1.87x – nearly double the bandwidth as compared to DDR4-3200.
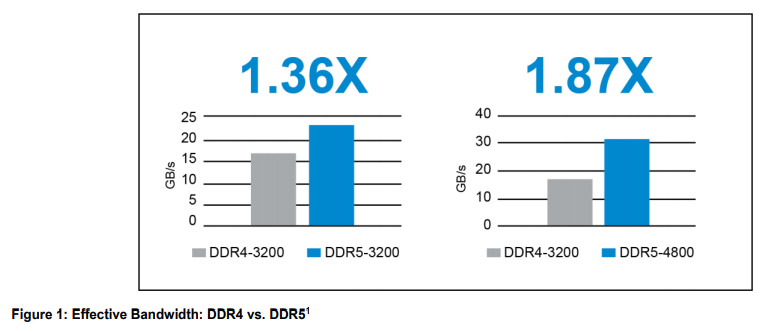
(source: Micron)
Memory companies need to be at the leading edge of technology to be able to support these high compute requirements.
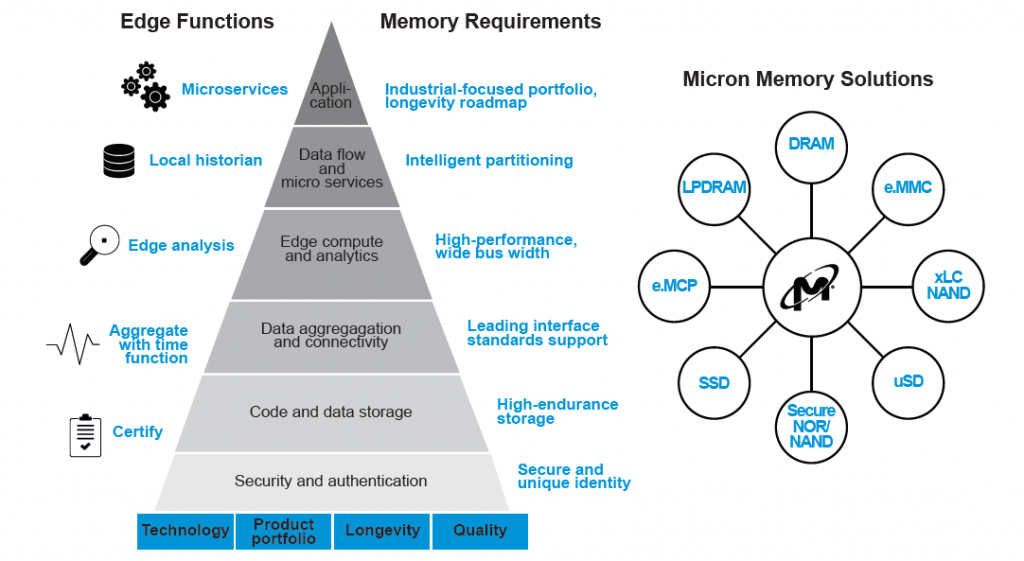
Code and data storage will need to accommodate the increased demand in these new applications. Popular IoT edge platforms typically require from 100 Mbytes up to 250 Mbytes of code storage at its base without any messages. And as new services are required, on-board data storage will vary from managed NAND solutions such as e.MMCs, up to TB level industrial/automotive PCIe NVMe SSD embedded solutions in micro-datacenter systems to support the edge data ingested.
Memory does play an essential role in edge solutions. From high performance DRAM with wide bus width and efficient throughput, to managed NAND and SSD solutions, to the need for a portfolio of industrial-focused solutions. All these need to be part of design tradeoffs and use case considerations.
Winning the Race to the Edge
Since edge solutions are a combination of hardware resources as well as edge software platforms, companies will need to look beyond their core competency, and expand their ecosystem for a more integrated solution offering. Partnerships between cloud providers, compute and enterprise network OEMs, industrial networking companies, as well as software application providers will be key to success. As the marketplace players strive to win this “race to the Edge”, we will see more partnerships, consolidations, and specializations all to try to seek new revenue streams from this new Edge frontier, and memory technology will be essential in every solution.

Author of this post:
Wil Florentino
Wil Florentino is a senior segment manager in Micron’s Embedded Business Unit, where he helps to spread the word about the Micron industrial memory and flash storage portfolio innovations.










