Edge platforms continue to play a vital role in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. Businesses deploying IoT solutions recognise that many optimally designed IoT solutions, especially those in the industrial vertical, take advantage of one or multiple edge components, says Josh Taubenheim, IoT technology analyst at MachNation.
In fact, MachNation research suggests that 85% of IoT solutions in verticals such as manufacturing, commercial transportation, building automation, and logistics will be required to leverage edge computing to meet business and operational requirements.
We spend a lot of time helping enterprises architect their edge solutions and then identify IoT platform vendors that can appropriately support these enterprises’ IIoT architectures. This is no small feat for two reasons. First, almost all edge solutions are incorporated into brownfield solutions. And second, there are many IoT platforms that support edge, however, not all of them do it well.
Let’s look at the differences between thin and thick edge and then provide some thoughts about relevant IoT platform vendors that support edge deployments.
Thin vs. thick edge
The complexity and implementation of edge technologies can vary widely. An enterprise’s IoT use-case determines the edge hardware requirements. According to MachNation research of enterprise IoT buyers, roughly 90% of the complexity at the edge is software-related. Thus, while many hardware vendors already provide hardware that adequately supports most IoT solutions, the quality, sophistication, usability, and scalability of vendors’ software and platform for both thin- and thick-edge deployments remain a differentiator.
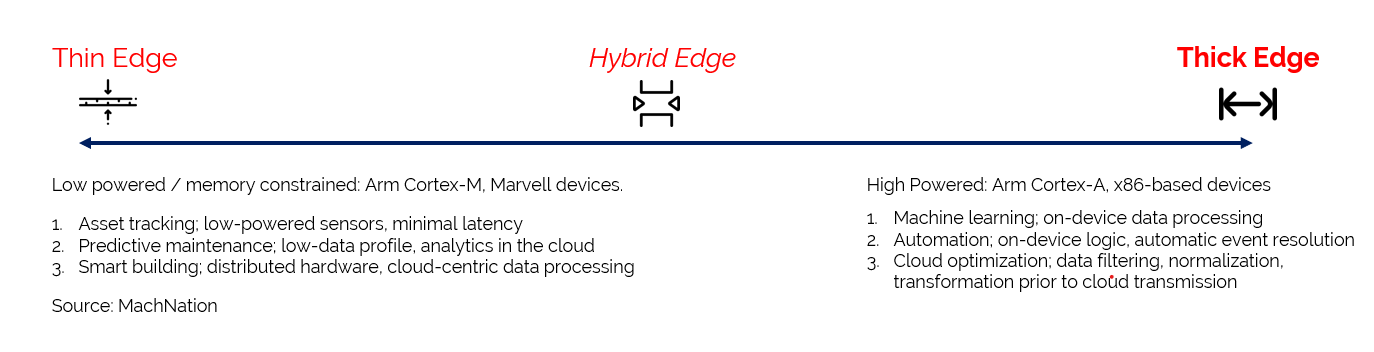
What’s the difference between thin-edge and thick-edge?
Thin-edge: MachNation defines a thin edge as an IoT solution supporting and managing decentralised deployments of low-powered, memory and power constrained devices, examples of which include Arm Cortex-M devices, low-power Texas Instruments (TI) devices, Marvell Technology devices, and others.
These devices transmit data northbound with minimal execution of workloads (e.g., filtering, aggregation, or normalisation) or analytics being performed at the site of data origin. Enterprises install thin edge nodes to connect legacy equipment to their cloud solutions, thereby taking advantage of cost savings on equipment.
Typical thin-edge use cases include:
- Geographical asset tracking; low-powered, continuous transmission to cloud
- Predictive machine maintenance; data points on machine health, monitoring
- Smart city / building; distributed hardware on a centralised network transmitting targeted data points
Thick-edge: MachNation defines thick edge as an IoT solution supporting and managing high-powered, high-capability edge hardware, examples of which include high-powered IoT gateway devices from companies like Dell and Cisco, Arm Cortex-A devices, x.86-based devices, and others.
These devices can run advanced on-device inference, event processing rules, business logic, analytics, and machine learning algorithms.
Typical thick-edge use cases include:
- Advanced machine maintenance; on-device anomaly detection, analytics, and parameter-defined event processing actions
- Automation; local logic execution, on-device analytics, data normalisation
- Cloud optimisation: reducing cloud-overhead by performing data management functions on-device (e.g. filtering out “junk” data before transmitting to the cloud)
MachNation’s evaluation of IoT edge platforms
For the fifth year, MachNation has published its IoT Edge ScoreCard to aid enterprise, system integrator (SI), and service provider (SP) buyers in their research processes and to provide guidelines for the most important edge characteristics. We have conducted these analyses due to the great diversity in the quality of edge platforms and the technological heritage of the various platform vendors.

MachNation’s 2022 IoT Edge ScoreCard rates vendors against the requirements of best-in-class software, hardware, and hybrid approaches to edge. MachNation recognises that today’s edge vendor landscape is both nascent and vibrant – offering myriad viable value propositions. As such, MachNation felt it important to include vendors that offer software-focused, hardware-focused, and hybrid offerings in this ScoreCard.
MachNation rated 12 IoT edge vendors across a set of requirements spanning four categories. The four categories of requirements consist of 19 sub-requirements that are the underlying bases of MachNation’s rating. The four categories are:
Edge data processing – IoT edge platforms should exhibit robust data processing capabilities. MachNation evaluates the robustness of IoT edge platforms on 5 key sub-requirements: data ingestion model, data normalisation techniques, data storage flexibility, rules engine sophistication, and analytics and visualisation capabilities. Edge platforms should have the ability to ingest data by offering extensive support for southbound legacy protocols (e.g., Modbus and PROFIBUS over RS-232) and contemporary protocols (e.g., PROFINET over Ethernet). An edge platform should enable remote configuration and management of data-normalisation functions, including the ability to apply statistical functions and custom algorithms to ingested machine data. In addition, an edge platform should provide a flexible data store and an event processor that can handle simple rules via declarative configuration and complex rules via scripting logic or custom code.
Edge management – IoT edge platform vendors should build their platforms with sophisticated edge management capabilities. Edge management sophistication is demonstrated when vendors focus on providing excellence in 5 key sub requirements: remote configuration, remote software management, connectivity management, deployment, and autonomy. The platform should have a set of features that empower an operations technology (OT) user to easily manage an IoT deployment.
Architecture and integration – MachNation believes that the best IoT edge technology should exhibit a cogent architecture with robust integration capabilities. Platform microservices should be built with both developer and user in mind. Integrations – pre-built connections to external enterprise systems and applications are found in virtually every IoT solution and thus provide significant value for ease of deployment and manageability. When evaluating the cogency of the architecture and the integration model, there are 5 sub-requirements MachNation evaluates: a security model; flexible cloud and local integration; platform productisation; a live edge marketplace; and the overall developer experience.
Strategy and business – Best positioned IoT edge vendors will have a well-developed, appropriately sized business and a sound IoT strategy. All other things equal, a successful IoT edge vendor will have extensive financial and human resources to support edge development and sales efforts; understanding of key IoT trends and customer needs; and a cogent, focused, and forward-thinking business vision that relates directly to the geographic market, customer segments, and industry sectors served by the edge vendor.
A IoT edge platform vendor excels in each of MachNation’s four evaluation categories with particular emphasis on providing exceptional technology, a refined user experience (UX), and strong documentation.
MachNation’s 2022 IoT Edge ScoreCard includes the following vendors (listed alphabetically): ADLINK, Amazon, IoT.nxt, Eurotech, HPE, Losant, Microsoft, Pelion, ThingsBoard, Siemens, Software AG, and ZEDEDA. MachNation selected a group of participating vendors that adequately represent the diversity of approaches and sizes in this burgeoning IoT edge market. MachNation’s research and testing team chooses participants that provide a mix of approaches for thin- and thick-edge solutions.
Conclusion
To summarise, the distinction between “thin” and “thick” edge boils down to where the data processing occurs and where actionable intelligence is generated. Every IoT edge deployment should be purpose-built to fit the use case. Restrictions on available hardware and software can also be determining factors. It is the recommendation of MachNation to have a well-defined hardware and software strategy in place before embarking on an IoT edge journey.
Choosing an IoT edge vendor comes down to multiple factors:
- Use-case
- Hardware availability
- Cloud infrastructure to support your edge solution
- Requirements around data latency, and other on-device compute resources
MachNation recognises the importance of edge technology in the IoT industry. Because of that we have chosen to dedicate an annual study of IoT edge vendors that offer edge solutions.
The author is Josh Taubenheim, IoT technology analyst at MachNation.
Comment on this article below or via Twitter: @IoTNow_OR @jcIoTnow










