Among the countless surveys covering the IoT ecosystem today, many will highlight how customers experience challenges related to connectivity for their deployments and that these challenges often result in the projects’ failure. Kaleido Intelligence felt that this particular area needed to be addressed. The result of this was the largest enterprise survey to date, with nearly 760 responses, focusing entirely on cellular IoT connectivity.
The results, published in Q2 2022, were enlightening. In order to obtain a complete picture of the connectivity landscape, respondents were split between those who had already adopted cellular technology for their IoT deployments, in addition to those who had not yet adopted the technology.
Several overriding themes emerged from the survey results, highlighting the challenge that exists in the ecosystem today:
Complexity
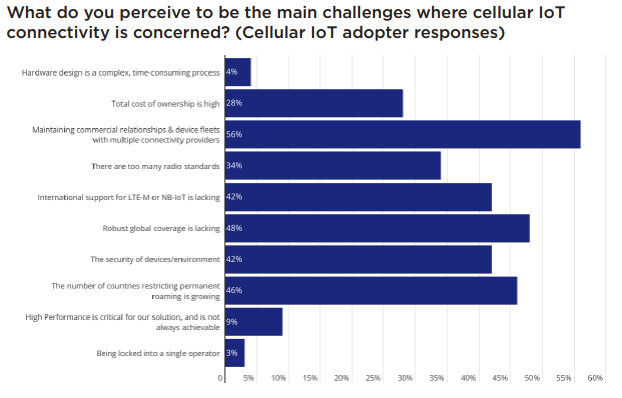
The cellular IoT market is unfortunately littered with issues that raise the complexity enterprises face in navigating the market. There are substantial barriers to overcome for those considering using cellular technology for IoT, in addition to those wishing to scale up their existing operations.
For non-adopters, overcoming hardware design complexity was cited as the number one barrier to market entry, by 84% of the market. To date, there are very few cellular IoT connectivity providers that can offer expertise and guidance in this domain, and with 3GPP standards and best practices being unfamiliar territory to the majority of enterprises, it is evident that an opportunity for connectivity service providers is not being maximised to its full potential.
For those adopting cellular IoT, 56% of respondents felt that ecosystem barriers were created due to the need to engage with multiple connectivity providers to address their international connectivity requirements. Coverage, commercial flexibility and quality of service (QoS) all factor into these concerns here, but the ideal is for customers to use a single provider for all of their cellular connectivity needs.
Roaming
In the world of cellular IoT, roaming plays a significant role in supporting international connectivity efforts. In Europe for example, over 50% of IoT connections are roaming on an inbound basis – with connectivity supported by an operator located outside of the country of operation. Kaleido’s surveys have found that 42% of mobile network operators (MNOs) and mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs) report that more than a quarter of their customers require international connectivity for IoT projects.
For operators receiving IoT devices onto their networks, challenges arise in the fact that devices often consume little traffic that can be monetised, while still consuming signalling traffic, which in turn requires investment into computing capacity. Regulators and operators alike have, in some countries, adopted hostile attitudes to the practice of permanent roaming, typically defined as such when an IoT device is registered on a foreign mobile network for more than 90 consecutive days. These attitudes can either consist of outright bans of permanent roaming, or present an underlying risk to IoT customers that, in the future, their device fleets may be at risk of losing access to the networks they require.
The risk associated with permanent roaming is clearly top-of-mind for many enterprises: the ability to offer solutions around this was ranked as the second most important capability for connectivity service providers to have by those adopting cellular IoT.
Security
Unsurprisingly, security was another key theme for cellular IoT connectivity: 59% of adopters ranked end-to-end security as their number one priority for deployments. While cellular technology is well-known for its security, notable gaps continue to exist today, particularly in scenarios where devices are roaming. This, coupled with inexperience or a lack of expertise to execute security best practices where application, device and data security are concerned, can lead to considerable issues for enterprises in the context of security risk. With 42% of cellular IoT adopters stating that the security of devices or the environment was lacking, it is apparent that there is an opportunity for service providers to take steps to address this gap; however, many connectivity providers offer little to no features where identification or mitigation of security threats are concerned.
eSIM
Embedded universal integrated circuit card (eUICC) embedded SIM (eSIM) specifications have been developed by the GSMA to afford customers a level of flexibility in their choice of connectivity provider, by virtue of enabling the SIM card to be remotely programmed over-the-air (OTA) to switch network providers. However, the majority of IoT devices using eSIM remain in insurance mode in the field: that is to say, they have never used the OTA network switching capability envisioned by the GSMA, on account of commercial, legal and technical challenges making network switching a long and arduous process. This was reflected in the survey, with 46% of those that hadn’t used eSIM stating that it is either simpler or more cost-effective to utilise other solutions, such as global roaming SIMs or multi-international mobile identification (IMSI) SIMs for their connectivity needs.
Private LTE/5G
Private cellular networks have risen to the fore over the last few years as a means of making use of the near-fibre performance levels of LTE and 5G in conjunction with the flexibility of a wireless communications solution. However, it was evident from the survey that a large proportion of enterprises still remain unsure of how to navigate the market, as well as being unsure of the technology itself. More than 60% of the survey respondent base stated a need for expertise when choosing devices and configuring networks, while 52% of respondents claimed they were unsure of how suitable private LTE or 5G would be for their organisation’s needs. It is evident that there is much work to be done on educating the potential customer base and guiding them through the procurement and deployment phases.
Trends shaping 2023 and beyond
Although cellular connectivity continues to form a relatively small proportion of the overall IoT installed base (approximately 17% in 2021), the technology has seen its market share grow over the years, with around 14% of the total IoT installed base using cellular connectivity in 2020. Meanwhile, significant growth over the coming five years is expected, in spite of ongoing chip shortages, supply chain constraints and economic headwinds.
Undoubtedly, Covid-19 has had a real impact on the cellular IoT market in the context of accelerating business digitisation strategies. Remote asset monitoring and tracking, automation, in addition to healthcare have seen upticks in demand as a result of the pandemic, while new service areas and technologies, such as private LTE and 5G in addition to growing narrowband-IoT (NB-IoT) and LTE-M coverage worldwide have helped address the variable connectivity needs required by enterprise customers.
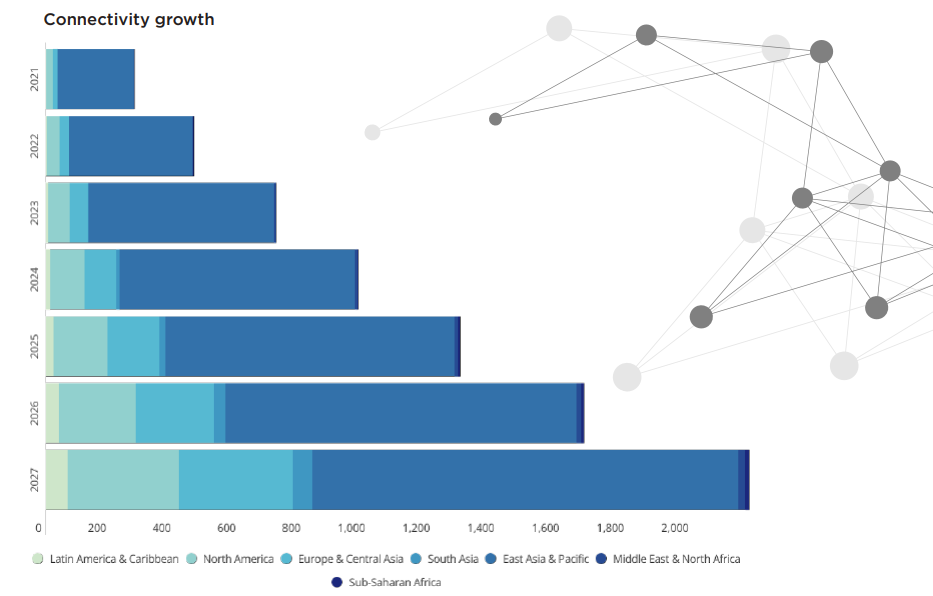
A significant proportion of future cellular IoT connectivity growth is expected to be fuelled by licensed low power wide area networks (LPWAN) such as NB-IoT and LTE-M. Kaleido forecasts that some 2.2 billion cellular IoT connections will use licensed LPWAN in 2027, up from 162 million in 2020. Devices using these radio access technologies (RATs) require a different approach to deployment and management:
- International roaming agreements for NB-IoT and LTE-M are far from pervasive, despite the good progress made by some tier one carriers. This means that service providers must be in a position to provide expert advice to customers in terms of how coverage is rolled out, support for power-saving features such as power saving mode (PSM) and extended discontinuous reception (eDRX), in addition to providing an understanding of total cost of ownership in relation to device and connectivity costs.
- Billing modules for communications management platforms (CMPs) must be adapted to meet the changing requirements for LPWAN monetisation. Increasingly, charging is no longer based on traditional MB-consumption models, but on network access fees, number of messages transmitted and others. Rating and charging systems must be flexible to accommodate several new business model types.
Network coverage both on a geographical scale as well as from a service provider footprint perspective is additionally becoming a key topic within the industry. Over the coming years, customers will no longer expect to see cellular technology support offered in isolation by providers. In this context, the development of the 3GPP’s Release 17 non-terrestrial networks (NTNs) offers a significant milestone in helping enable that vision, with several service providers emerging to offer NB-IoT support through direct-to-satellite connectivity. While the market for NTN is at a nascent stage, and has yet to prove itself as a scalable and profitable solution, work towards mechanisms to assure robust global coverage for IoT customers is being generated by both the supply side for IoT connectivity; Kaleido has had several discussions with mobile operators on this topic; as well as the demand side, particularly for customers with connectivity needs in areas either underserved or unserved by existing terrestrial networks.
Private mobile networks can, in some instances, address the coverage gap experienced by end-customers, particularly where no backhaul to centralised servers is needed or required. However, where NTN may address and expand upon the non-critical side of IoT requirements, private networks offer the potential for guaranteed quality of service, high performance and the ability to address key business needs in a manner that public radio networks cannot. As costs for 5G devices and network components continue to fall, it will become an increasingly important economic factor in technology choice for private networks, given equal or better performance versus private LTE with fewer network components required. Kaleido expects more than 12,000 sites will use private 5G by 2027, with deployed sites growing by an annual average of 137% per annum.
2023 Survey
It is apparent that the connectivity service provider ecosystem cannot stand still given the considerable challenges posed for the enterprise market. As such, Kaleido will relaunch its enterprise survey for 2023. This year’s survey will aim to understand how enterprise perceptions towards the challenges uncovered in the 2022 survey have shifted over the past year, as well as aiming to delve deeper into how ecosystem players can best address the needs of the market. Where are the opportunities beyond connectivity? How can connectivity service providers best position themselves for the needs of specific industry verticals?
The survey results will give a clear indication of where enterprises, across high growth vertical sectors, are with connectivity strategies. The analysis will help pinpoint the evolving needs, challenges, success stories and priority areas that the ecosystem as a whole must address to help all stakeholders move forward in enabling results driven seamless connectivity solutions.
Be prepared for a wealth of new insight, use cases, industry education and direction come May 2023 to help shape your connectivity strategy.
Comment on this article below or via Twitter: @IoTNow_










