In this article, Robin Duke-Woolley, Analyst and CEO of Beecham Research, shares his latest insights from the Healthcare and Life Sciences sector on the key issues facing the market and how IoT is addressing them.
Introduction – towards a continuum of healthcare
The use of IoT in the healthcare sector is in rapid growth and has been substantially affected by the Coronavirus pandemic, which has placed unprecedented stress on healthcare systems worldwide.
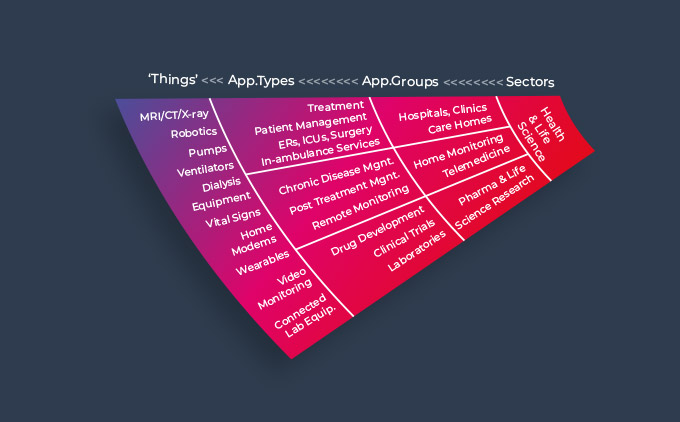
Beecham Research’s work in the healthcare sector is based on a continuum of medical care across a patient’s journey from illness to wellness. The stages where care is given are:
- ambulance/emergency room when a patient first falls ill and taken into hospital to undergo acute care
- Resident in-hospital stay where curative treatment is given
- Care home/nursing home where patients receive rehabilitation or long-term community care
- At home care for long-term chronic disease, with the patient being actively involved in conjunction with the patient’s doctor
- GP and other surgeries – including services like health checks, optometry, dentistry
- Pharmaceutical research and clinical trials for developing new treatments, vaccines etc.
This continuum of care across different care settings include general practice, acute care, community and social care, mental health, and hospice-based care. It is noteworthy that each of these care settings involve treatments given by trained personnel specialising in different types of treatment, supported by specialist equipment.
These are all areas where the application of IoT technologies can make a real improvement to patient outcomes and service performance. Benefits include reduced time needed for a correct diagnosis, accurate treatment identification, cost reductions and efficiencies improvements to all parties, and faster development of new medicines and vaccines.
During the pandemic in particular, telehealth or remote care has grown through the use of remote connectivity technologies. For example:
- Remote GP examinations have replaced many face-to-face visits. Working from home is commonplace, allowing practitioners to offer vital services like GP appointments or mental health support accessibly and safely.
- While the clinical environment has been the primary setting for health care, remote connectivity offers new options previously not available or used to their full potential. This unlocks both organisational efficiencies and additional services and benefits for patients.
- Increased remote monitoring of patients at home with chronic conditions include conditions like diabetes, where readings of vital signs are taken through wearables and sent over the air to the surgery.
1. Key Issues in the Sector
- The use of connected wearables for healthcare is well established for the remote monitoring of chronic diseases, for example diabetes and heart disease. During the pandemic, nursing staff caring for infectious patients in hospital were helped by vital signs being transmitted remotely to a screen away from the patient.
- Telehealth solutions aim to provide required monitoring remotely without reducing patient support. Moreover, care givers need to feel supported, with plenty of touchpoints with other team members. The healthcare sector is seeing substantial growth in use of connected devices, and this is expected to continue.
- However, flaws in the way treatment is delivered have been highlighted. Patients sometimes are subjected to different treatments in different locations as well as in different types of establishment. The information collected at each of these may be recorded in different formats and not easily accessible by practitioners caring for the patient at any point across the complex supply chain. This data could be very diverse and could include both data sent from IoT devices as well as manually entered readings.
- Moves are underway to create a common accessible electronic health record (EHR) that would facilitate the delivery of integrated care. Joined up care systems will save healthcare professionals valuable time accessing key medicines information, provide clinicians with access to a richer source of information consistent across all care settings and, in turn, help reduce errors and improve patient safety.
2. How IoT is addressing these issues
Delivering care where and when it is needed is made possible through reliable, flexible and cost-effective connectivity, supporting care practitioners with faster, more reliable access to the information and services they need, when they need it. For example,
- IoT can help transform the ambulance into a remote consulting room, by enabling paramedics to conduct on-board treatments via mobile expert consultation, saving valuable time while easing the strain on hospital resources.
- A ‘smart hospital’ is an advanced facility where everything is tracked and managed simultaneously while all the data is collected in a centralised database. Many are moving towards the next stage of ‘smart healthcare’, which involves cross-hospital collaborative healthcare. Digitalised asset tracking makes sure the right equipment and facilities are in the right place at the right time, and that the patient’s location is always known as he/she moves through the hospital to receive different treatments.
- Planned predictive maintenance of equipment and machinery can spot warning signs of problems before they occur.
- Patients residing in care homes may not need hospital admission but still need medically qualified staff to be on hand. Remote monitoring has proved its value in this setting too.
- A large proportion of sufferers of chronic diseases are benefiting from home-based remote healthcare, supporting independent living. So-called ‘Hospitals At Home’ are now common in many countries.
- For other specialist clinics, such as dental and ophthalmic clinics, non-invasive digital diagnostic tools are proliferating.
- Concern over mental illness has been on the increase, particularly since the virus lockdown. Chronic disease sufferers often also suffer from depression and anxiety. Here again, digital tools are finding use for therapy and the prevention of escalations.
3. How the IoT World Map can assist
IoT solutions have several different elements and can be complex. This complexity will also increase with more use of real time processing, the introduction of private networking and the rollout of 5G. Each of these offers major benefits in this sector but assistance from IoT solution experts with specific knowledge of the healthcare sector will increasingly be needed. This presents a difficulty for IoT buyers, who typically have to identify which suppliers have specific knowledge of their application areas.
The IoT World Map is arranged so that those requiring IoT solutions can access the map knowing only the applications they need support for in their own sector. IoT suppliers who have direct healthcare sector experience and can assist specifically in healthcare solutions can be readily identified and contacted.
The aim of this is to assist IoT buyers to proceed more quickly to solution design and implementation.
Robin Duke-Woolley
Beecham Research