With the increase of IoT devices, one needs solution to connect, collect, store, and analyse the device data. Amazon Web Services provides various services that helps connected devices to easily and securely interact with cloud applications and other devices for various user scenarios.
Migrating or designing Internet of Things (IoT) solutions on to AWS platform enables one to focus on core business without the hassle of infrastructure management and monitoring. This will ensure high availability to the customers. If the right AWS services are used for customer requirements, then IoT solutions will be able to deliver results in a more secured, reliable, and scalable manner, says Chandani Patel, Tech lead at Volansys Technologies.
Design to reliably operate at scale
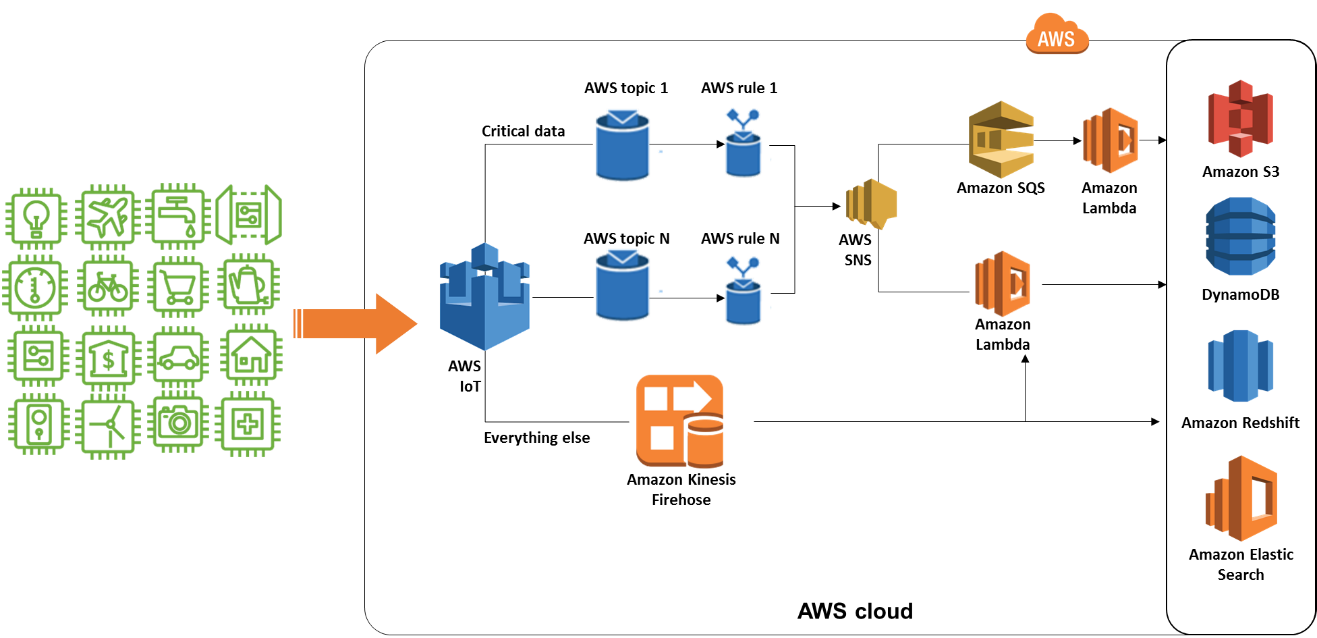
IoT systems must handle high-velocity and high-volume data captured by devices and gateways. The cloud system architecture should be scalable to handle overflow of data. The best approach is to send data to queue, buffer or real-time in-memory databases before storing it in storage.
The device can publish data to AWS Kinesis, or AWS IoT rule can be used to forward data to AWS SQS and Kinesis to store it in time-series stores like AWS S3, Redshift, DataLake, or Elasticsearch for data storage. These data store can be used to generate custom dashboard or AWS QuickSight dashboards.

Route large data volumes through data pipelines
The most secure and best way to ensure all data is processed and stored is to redirect all device topics data to an SNS which is designed to handle data flood processing, ensuring that incoming-data is reliably maintained, processed and delivered to the proper channel. To make it more scalable, multiple SNS topics, SQS queue, Lambda for a different/group of AWS device topics can be used. One should consider storing the data in safe-storage like a Queue, Amazon Kinesis, Amazon S3, and Amazon Redshift before processing. This practice ensures no data loss due to message floods, un-wanted exception code or deployment issues.
Automate device provisioning and upgrades
AWS IoT provides a set of functionalities which can be used for batch import with a set of policies that can be integrated with dashboard or manufacturing process where a device can be pre-registered to AWS IoT and certificates can be installed in the device. Later, device provisioning flow can claim device and attach with user or any other entity. AWS provides the facility to trigger and track OTA upgrades for devices.
Designing built-in capabilities within the device for automated provisioning and leveraging the proper tools that AWS provides to handle device provisioning and management, allows systems to achieve desired operational efficiencies with minimal human intervention
Adopt scalable architecture for custom components
As IoT system connects to external world devices, the scope doesn’t end by connecting, controlling and reporting of devices. Think about adopting the latest technologies like Data Science and Machine Learning or integrating third party components in IoT system like IFTTT, Alexa or Google Home. The Architecture of IoT should ensure that the external components can be easily integrated to solution without any performance bottlenecks.
Check for offline access and processing
Sometimes it is not necessary to process all your machine data in the cloud. In many cases there is no continuous internet connectivity available. For such a scenario, add AWS Greengrass at the edge. Greengrass processes and filters data locally on edge and reduce the requirement to send all device data upstream. One can capture all data, hold it for limited amount of time and send it to cloud on error events or on demand/request. If there is a need of time-series data, then one can schedule a periodic process that sends device data to cloud which can be used for future enhancements like AWS Machine Learning models and cloud analytics tools.

Right data storage selection
IoT systems generate high-speed, high-volume, and variety of data. Each IoT device or device topic can have different formats, which may not be manageable through a single database or a similar type of data-store. Architect should be careful while choosing database format and data-store. Sometimes single data-store works fine, or hybrid data-store for different purpose helps to achieve high throughput. Frequently used static data can be stored in the ElastiCache which helps to improve performance. Such practices help to achieve scalability and maintainability of the system.
Filter and transform data before processing
All incoming data to IoT system may require processing or transforming, after which it can be redirected to storage as it is. AWS IoT rule provides action to redirect messages to different AWS services. An Architect should dive all data in different forms i.e. processing-needed, ignored/static data (like Config) and direct storage.
AWS IoT helps to achieve quick device connectivity, secure data ingesting, easy device management, multi-protocol support and much more.
The author is Chandani Patel Tech lead, Volansys Technologies
About the author
Chandani is working as Tech lead at Volansys Technologies. She is an AWS Certified Solution Architect, AWS Business & Technical Professional enabling cloud solutions, IoT solutions and ML/Data Science. She is Cloud Solution Architect with deep expertise in designing, developing and architecting cloud solutions for public clouds (Azure, AWS, Google & Bluemix), private clouds and hybrid clouds.
Comment on this article below or via Twitter: @IoTNow_OR @jcIoTnow










