Smart metering is being rolled out in many advanced economies but this is one of those times when lessons may best be learned from an emerging economy, in this case India.
In this exclusive interview, Jeremy Cowan talks to John Cronin, executive chairman of CyanConnode, about the lessons of interoperability, security, simplicity and collaboration.
IoT Now: What is India teaching us about the future of smart metering and the Internet of Things (IoT)?
John Cronin: Global demand for energy continues to rise and meeting the demand cost-effectively means investing in new technologies that increase efficiency. Governments, city authorities and businesses are looking to find ways of achieving more efficient management of devices such as utility metering.
In India, the adoption of smart metering is driven by the need to reduce current Aggregate, Technical and Commercial losses, which are equivalent to US$32 billion, as well as connect 240 million people without electricity. To address these challenges, the Indian government has approved the UDAY scheme, which aims to deliver the financial turnaround for utilities and has a target to install 35 million meters by 2019.
Smart metering solutions, such as Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), provide bi-directional communication between consumers’ meters and utilities. AMI technology enhances utilities’ service delivery, improves business efficiency and saves energy through improved revenue collection and cash flow.
However, delivering robust AMI solutions requires a complex ecosystem, including government, regulators, meter manufacturers, technology providers and system integrators. Each element, from meter to application platform, of this critical infrastructure needs to be validated, and must work together seamlessly. Like all critical infrastructure, it is imperative to minimise the vulnerabilities in each element to deliver a secure system.
CyanConnode’s enabling technology is delivered through a collaborative engagement model. The company has established a market-leading position with a strong partner ecosystem which includes meter manufacturers and system integrators. CyanConnode’s proven technology and expertise in system integration ensures it can provide a robust solution from meter to the application platform, working with and across any third-party technology thanks to its standards-based, technology-agnostic design.
Selecting a sustainable, cost-effective solution is key to delivering a system that is suitable for the environment and meets market requirements. Smart metering solutions deployed in next-generation economies such as India must cost as little as possible to manufacture and operate. In addition, they must be able to work in densely populated urban environments as well as on the fringes of the electricity network.
The Ministry of Power in India, through institutions such as the National Smart Grid Mission and Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), has accelerated the implementation process and analysed the benefits of Smart Grid Technologies, such smart metering, OMS, PLM, PQM, and Microgrids. Following this research and analysis, the BIS has created standards for metering, the communication network and AMI systems, deeming IPv6 and 6LowPan mandatory technology for RF mesh communication in India. CyanConnde’s Omnimesh product addresses the requirements set out in these standards.
The key things that India is, therefore, teaching us about the future of smart metering are:
- Interoperability is mandatory
- Security is imperative
- Simplicity is key, and
- Collaboration is the way forward
IoT Now: If the number of IoT devices and nodes are going to be in the billions, then a lot of space and energy is needed for IoT. Can you quantify what design miniaturisation is enabling in smart metering now that wasn’t possible 2-3 years ago?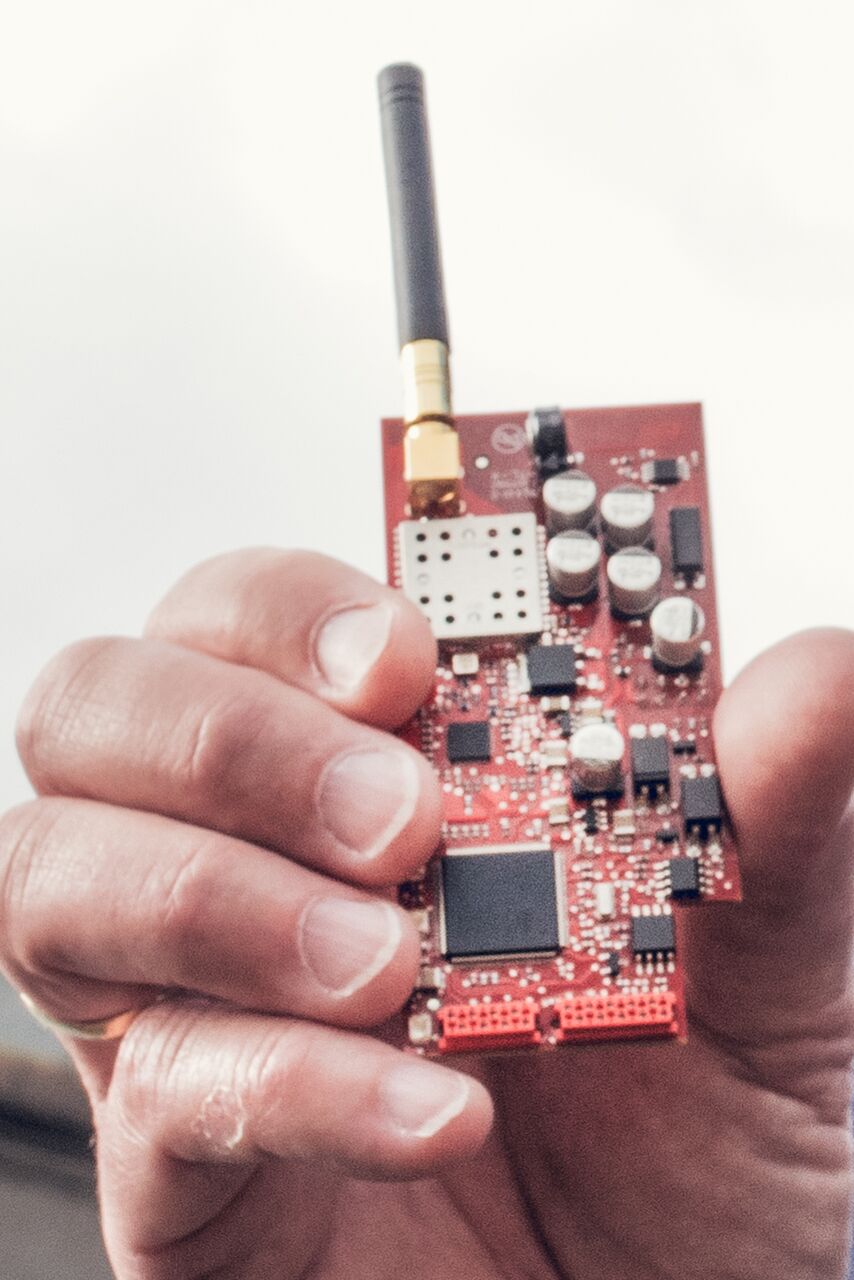
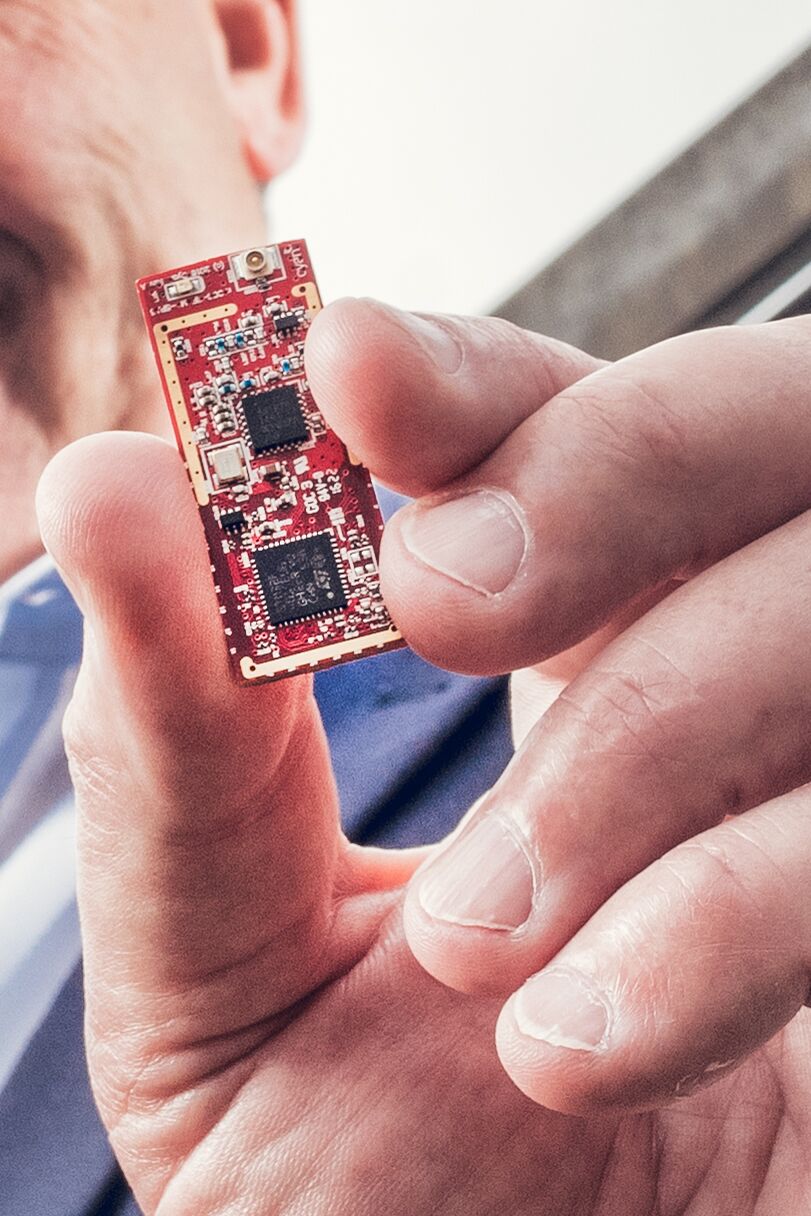
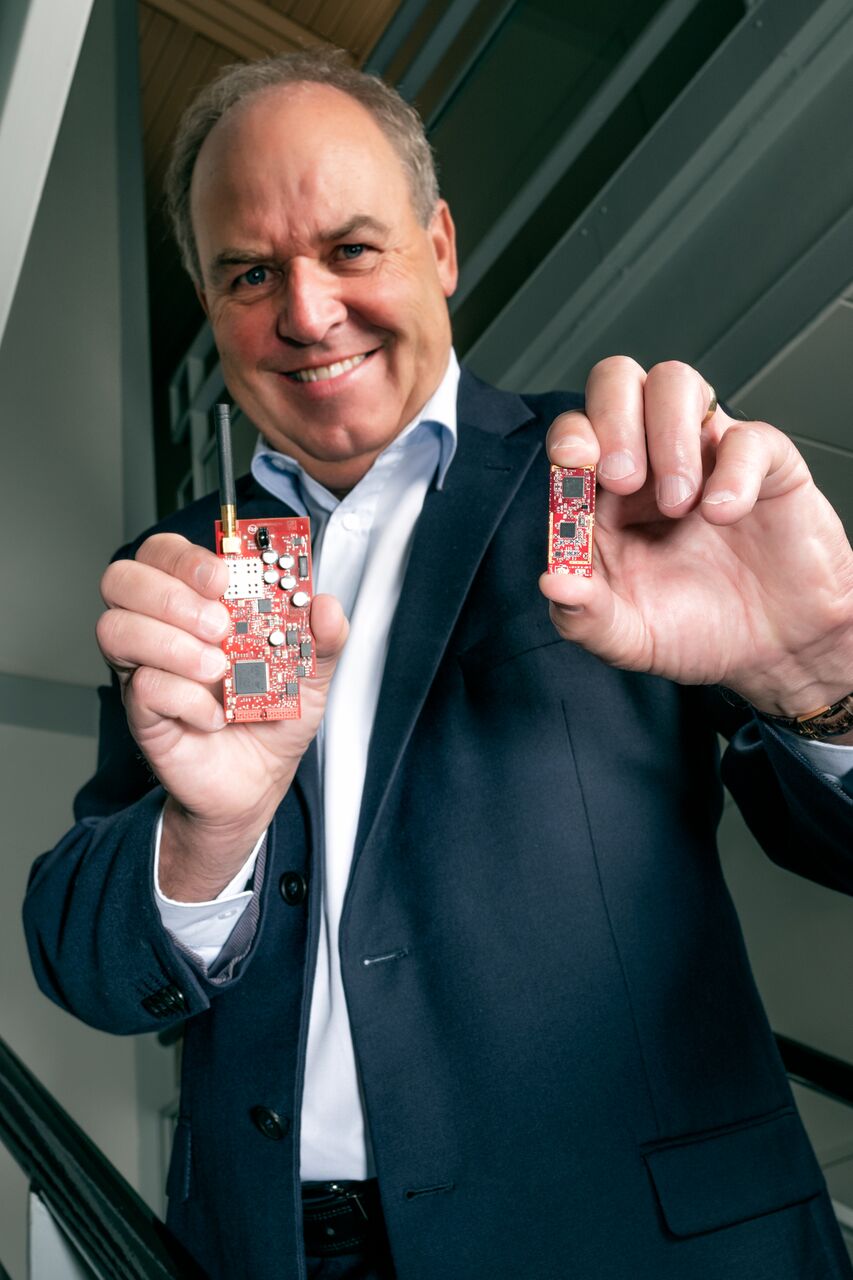
[Picture of original Connode node + CyanConnode IPA3 node]
John Cronin: Electricity meters are space-constrained, must operate within regulatory power limits, and must compete in a competitive, cost-sensitive market. Small, power-efficient hardware is critical to unlocking smart metering and numerous other markets.
Standards maturity is a key enabler. They have allowed silicon vendors to build multifunction System on Chips (SoCs), which integrate IPv6-supporting, secure, sub-GHz, IEEE 802.15.4 radio transceivers with capable embedded ARM processors. Together with production process improvements, integration has produced smaller, lower power devices that weren’t possible a year ago.
Once the communication technology is in place, standards develop the market and present new business innovation opportunities. For example, a standards-compliant AMI system can reduce energy use, increase revenues, and drive beneficial consumer behaviour by delivering critical peak-pricing tariff information to meters in real time.
Bringing the off-grid population on to the grid has been shown to improve quality of life and bring economic benefits, but traditional post-payment electricity billing models are unsuitable for the majority of the population in many countries and blocks the electrification progress. To identify a single technology that could change people’s lives most it is prepayment. An AMI system, such as CyanConnode’s Omnimesh, which supports energy usage collection and prepayment token transfer enables electrifications and the new on-grid energy consumers realise the benefits.
CyanConnode also sees interest from communication infrastructure providers to offer smart metering as a service. Some IoT applications cannot start because the CAPEX/OPEX costs of installing and running a dedicated communication infrastructure are too high. By running these IoT applications alongside smart metering on the same communication network everyone’s costs are reduced. For true multi-application solutions to succeed more standardisation work is required on security and network management.
IoT Now: What is the current situation in your deployments in India and elsewhere? And what are the lessons for the sector as a whole?
John Cronin: CyanConnode has been working in India since 2009 and has established CyanConnode Private Ltd, which includes a local team of sales, project delivery and technical staff. The company has gained great success in smart metering deployments in India and so far has the highest number of smart metering projects on RF mesh communication in India.
The company started its India journey with Proof of Concepts (PoCs) to showcase the strength of its technology and enthusiasm to work in the Indian market. Following PoCs in multiple utilities, integrations of its RF mesh module with multiple meter manufacturers, and the establishment of a local team and office, CyanConnode has strengthened its presence across India.

Working with local partners, CyanConnode has installed its technology in several customer deployments in India, including: Chamundeshwari Electricity Supply Corporation Limited (CESC), Tata Power Mumbai, Uttar Gujarat Vij Company Ltd (UGVCL) and Madhya Pradesh Paschim Kshetra Vidyut Vitaran Company Ltd (MPWZ). UGVCL is currently observing data availability of over 99% in its smart metering deployments.
CESC was the first of 14 smart grid pilots to be rolled out in 2017 under the Smart Grid Task Force in India. The contract to install AMI was awarded to CyanConnode, through its partner Enzen, for the supply of 21,000 smart meters and associated hardware and software. As part of this deployment, CyanConnode supplied its RF mesh module to three different makes of meters and showcased the interoperability of different meter manufacturers on a single RF network. This is the first project in India to undertake this type of deployment. During implementation, this project has become a valuable reference for the wider Indian smart grid community and in July, Energy Minister DK Shivakumar inspected the first phase and confirmed that CESC will expand its smart grid project to the entire city. Furthermore, in January CESC officially confirmed that the formal milestone for User Acceptance Test was officially complete.
Following its involvement in multiple test sites and subsequent expansions, CyanConnode’s RF mesh Solution was deployed by Tata Power for their Mumbai Power distribution and is now integrated into approximately 17,000 smart meters. In parallel, CyanConnode deployed around 12,000 smart meters at Pashchimanchal Vidyut Vitran Nigam Limited (PVVNL), a power distribution company of western part of Uttar Pradesh.
Following the acquisition of Connode, the company received its first order from India for its new Omnimesh, cost-optimised IPv6 6LoWPAN-based, AMI solution. The solution has been rapidly integrated with Genus’ latest BIS compliant meter; with 10,000 meters deployed as of June 2018.
Ahead of the official launch in June, CyanConnode received its largest order to date for IPv6-based Omnimesh, from strategic partner Larsen & Toubro for a 25,100 unit AMI solution for MPWZ. This second order for Omnimesh highlights the strong value proposition of the product and the growing demand for standards-based solutions.
The lessons for the sector are that to deliver a complex, end-to-end solution requires an ecosystem of partners. The adoption of standards-based technology provides alignment of meter functionality and enables interoperability, which supports diversity of supply. It is clear to CyanConnode that using the strength of its communication technology as the back bone of a smart metering project will play a vital role in all large roll outs in India and, indeed, globally.
IoT Now: The industry has been talking about standards-based hardware and software for years. You say smart metering and IoT solutions are not equal; please explain.
John Cronin: Although for a single project a proprietary and open standards-based solution may provide the same level of functionality and performance, a standards-based solution has significant benefits when considering the wider context.
Standards-based solutions provide opportunities to streamline the integration effort by ensuring a greater level of interoperability between the components from different vendors, which is essential for the overall success of the project, from procurement to end-to-end integration.
Standards-based solutions also allow for knowledge sharing and use of common processes and tooling. This is particularly important when considering security. Open standards allow for greater peer review and shared work on threat model analysis, security model design, implementation and validation. This leads to more secure, reliable and performant systems which ultimately benefit both solution vendors and their customers.
Because of the knowledge sharing, standards-based solutions also improve longevity; allowing systems to be supported for decades, even if the original designers are no longer available. This has been a significant problem with proprietary systems of the past, as they quickly turn into legacy silos due to an inability to properly maintain them. For systems as critical as the management of a nation’s core infrastructure, this is fundamental.
However, in these early days of evolving standards, there is still room for vendors to differentiate their solutions. CyanConnode has spent a significant effort optimising the 802.15.4 / 6LoWPAN network stack to ensure it provides a best in class service, supporting unparalleled performance and reliability.

The CyanConnode Omnimesh platform also provides out-of-the-box solutions for managing the large device populations seen in smart metering projects. This includes secure and efficient features for large-scale delivery of firmware upgrades, time synchronisation and device configuration.
IoT Now: What is the role of Sub GHz spectrum for smart metering and IoT?
John Cronin: In urban areas, a sub-GHz standard performs most effectively, as the lower the operating frequency, the higher the transmission range for the signal. In simpler terms, operating on sub GHz frequencies ensures that the signal can easily propagate through concrete walls and reach further.
The optimum benefits can be achieved when smart meters are continually connected to other components of the network and the utilities; therefore range is important. Sub-GHz networks utilise frequency channels that are always available, and free of charge, unlike licensed spectrum that does not have pervasive coverage because it is not economically viable to have infrastructure to support the most rural areas. In addition, due to its range, sub-GHz systems require fewer access points to serve the same number of smart meters, thus reducing the cost of deployments.
The amount of data being collected from IoT devices is relatively small. Therefore, the benefits of a higher bandwidth solution, such as WiFi or cellular, are very limited. These also trade spectrum and power efficiency to achieve the higher bandwidth, meaning they are not well-suited to last mile IoT communications.
On the other hand, a Sub-GHz narrowband solution provides the perfect balance of spectrum and power efficiency, transmission range, bandwidth and low cost deployment model. This makes the Sub-GHz spectrum perfect for smart metering and IoT: great transmission range, readily available, free of charge and able to transmit small amounts of data quickly.
John Cronin, executive chairman of CyanConnode was talking to
Jeremy Cowan, editorial director of IoT Now and VanillaPlus.
Comment on this article below or via Twitter: @IoTNow_OR @jcIoTnow