Embedded SIM (eSIM) has emerged as a means to free consumers and connected devices from the constraints of the traditional, plastic subscriber identification module (SIM) card by enabling an eSIM or an integrated SIM (iSIM) to be embedded into a device at the point of manufacture and shipped globally.
On arrival at the location where it will be used, the device simply connects to the most suitable network operator in a process known as bootstrapping and the device is authorised to connect to the network, with the owner paying service charges.
That’s the theory at least, reality will involve some fragmentation and the need to select providers and manufacturers that can integrate or embed SIMs into devices, writes George Malim
What are the advantages of eSIM and iSIM?
The promise of this radically simplified process is an advantage for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) because it enables them to streamline the production process and have just a single stock-keeping unit (SKU) designation for a global product rather than having multiple variants for different global markets. They’ll also be able to play themselves into the connectivity value chain, potentially using their customers and the volumes of devices they make as a springboard to negotiate deals with connectivity providers that they can resell to customers.
User organisations will also benefit because they won’t have to install SIM cards into devices when they arrive at the point of use. In addition, they won’t have to configure simple devices for local markets, saving time and cost. These organisations won’t have to engage in complex vendor management processes nor have to commit to a single carrier for the life of the deployment. Instead, they will have flexibility to choose the best coverage at the best price for each deployment – and, in future, to shift operator when this is no longer optimal.
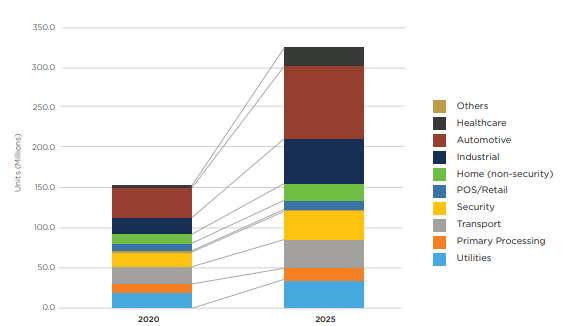
The eSIM revolution is already underway as Figure 1 shows.
How remote sim provisioning makes IoT devices flexible and secure
Strategy Analytics forecasts that sales of eSIMs for IoT applications will grow to 326 million by 2025.
One of the reasons for this projection, according to the firm is that eSIM offers the ability to change service provider profiles using remote SIM provisioning (RSP), without needing to physically change the SIM card itself, which is vital in enabling devices where it is either difficult or inefficient to access a physical SIM, for example hermetically sealed medical devices, vehicles, consumer electronics devices or a whole range of other IoT devices.
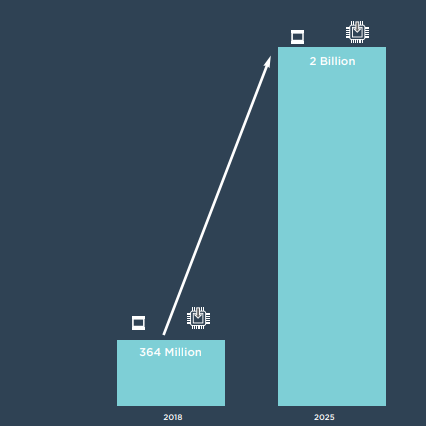
RSP also plays into IoT organisations’ desire not only to have flexibility but to have greater control of connectivity and to be assured of security for their devices.
Significant steps have been made in this respect with GSMA piloting development of the IoT SIM Applet For Secure End-2- End Communications (IoT SAFE), which aims to provide a standardised, globally accepted root of trust for IoT communications. Ensuring that eSIM includes a root of trust or secure element is therefore an increasingly important requirement and one which suppliers are responding to.
Traditional credentials, such as smart cards, will continue to account for the majority of market volume although the ability to create, access and share digital credentials, plus securing connected devices, will drive adoption of higher value solutions. Even so, adoption of eSIM in IoT is only expected to account for a small portion of overall eSIM adoption.
eSIM adoption by the IoT industry

Although it does not foresee the industrial and public sectors driving eSIM uptake, Juniper Research does see significant opportunities for the technology across industrial sectors.
A recent study by the firm identified the oil and gas, manufacturing and logistics sectors as three key areas in which eSIM adoption will ramp up.
eSIM installations in these verticals grow from 28 million units in 2021 to 116 million by 2025. The firm’s research also suggests that the development of rugged devices and appealing form factors will position vendors well to capitalise on the market.
In spite of this significant growth, Juniper Research believes it is the consumer sector that will account for 94% of global eSIM installations by 2025 and it anticipates that established adoption of eSIM frameworks from consumer device vendors, such as Apple and Google, will accelerate the growth of eSIMs in consumer devices ahead of the industrial and public sectors. The bulk of eSIMs will be installed in connected devices and these will increase from 1.2 billion in 2021, to 3.4 billion in 2025; representing a growth of 180%.
The research also uncovered that global eSIM deployments across all consumer verticals will increase by 170% over the next four years, with widespread adoption reliant on backing from network operators. Juniper Research therefore has urged device manufacturers to place pressure on operators to support eSIM frameworks and accelerate market maturation.
Global eSIM forecast for the 2020s
The fragmentation that exists between hardware vendors in the cellular IoT device market will require each vertical to adopt a combination of wireless technologies, hardware and management tools. In time, specialist vendors will emerge that provide robust eSIM form factors for industrial environments.
These, alongside eSIM and iSIM providers that adopt secure practices and enable the new SIM to become a root of trust, will empower IoT – as well as other sectors – with secure and flexible means to connect their devices with less friction and more choice than ever before.
With eSIM adoption already underway, it is expected to be adopted within smartphones, enterprise IoT and wearables, with integrated iSIM technology following by 2025.
Counterpoint Research has estimated shipments of eSIM-based devices will reach almost two billion units by 2025, up from 364 million in 2018, according to the latest research from the company’s Emerging Technology Opportunities Service. The findings also show that a majority of eSIM- based devices will have a hardware chip- based eSIM solution until 2025 and, after that, there will be a rise in the adoption of iSIM-based solutions.
What about the adoption of eSIM in smartphones?

Adoption of eSIMs in smartphones – again, the consumer market – is expected to drive the major volume growth while other connected devices such as mobile hotspots, routers, connected PCs, drones and smartwatches will grow at a higher CAGR because of their relatively smaller base of adoption today. However, in terms of shipment volumes, smartphones and B2B IoT devices will lead.
Counterpoint expects we will see a shift in adoption to the GSMA-compliant hardware-based embedded universal integrated circuit card (eUICC) for the next five to six years alongside iSIM or iUICC within system-on-a-chip (SoCs) devices across different device categories, replacing the less secure proprietary soft eSIM solutions. While hardware-based eUICC will be popular across smartphones, automotive, iSIM or iUICC will be popular across IoT applications.
Does eSIM reduce the risk of a changing connectivity market?
The arrival of eUICC creates an open standard by which connectivity can interoperate and be orchestrated for localisation. This is important for IoT organisations across several dimensions. At its most basic, it enables moving devices to shift location and even country without having to renegotiate for connectivity so it’s ideal for asset tracking across a market such as western Europe. That renegotiation could involve installation of a new physical SIM and makes several use cases unviable.
For less mobile, but still movable items, orchestration for localisation means a vending machine can be sited in a garage in Los Angeles and, if the location isn’t successful, it can be moved with no fuss to another location where the best mobile network may be from another provider. The vending company doesn’t have to worry about the connectivity, only its business case of making sure its machines go where the most customers are. This capability also takes away the risk involved in connectivity selection. If you know you can reconfigure device connectivity over-the-air, you know you are in control of your device. This is especially important for devices with long operating life expectancy that might be in the field for many years.
For these types of deployments, having to make network selections today for a device that might still be active in 2030 is a significant worry. No one knows what the connectivity landscape may look like then and being tied to a connectivity contract from 2020 provides no flexibility to respond to changing market needs.
A further concern that intelligent connectivity addresses are the dynamics of the global economy. Different countries impose different regulations and these could render certain approaches to connectivity obsolete. By having one connectivity platform for IoT, organisations can manage these changes by switching operator to ensure an approved form of connectivity is utilised. In addition, they are insulated from geo-political shifts such as if one country has a conflict with another.
How to select the right IoT connectivity partner for your IoT project
By adopting an intelligent approach to connectivity and selecting an IoT connectivity partner that understands the potential eSIM brings but also the need to manage different use cases in different countries in different ways, IoT organisations can ensure they are in a position to continuously have optimised IoT connectivity. Different countries have different regulations – Brazil, for example, does not allow permanent roaming for IoT devices, they can only connect using a local carrier.
Therefore, the possibility to keep connectivity streamlined by having a single connectivity platform from one provider is appealing. This platform provider can manage all the changes and handle all the integrations. In addition, deals of this type insulate the customer organisation from changes such as geo-political shifts that might cause an individual organisation to rethink its connectivity provision.
eSIM and iSIM are among the most significant innovations to arrive in IoT connectivity in the last ten years, it’s now time to engage with them and work out how to make them contribute to your IoT project.
This report first featured inside IoT Now magazine. Subscribe here for your free digital issue: https://www.iot-now.com/register/










