Europe is an early adopter of IoT and sustained, planned investment by enterprises will ensure it keeps its position as the third largest IoT market behind China and North America as the decade continues, in spite of the challenges of war and disease, writes George Malim.
The Next-Generation Internet of Things (NGIoT) initiative of the European Union reports that 80% of processing and analysis of data currently takes place in data centres and centralised computing facilities, and 20% in smart connected objects but this is poised to flip. Within the next five years, 75% or more of the data processing and analytics will run at the edge of the network. Within this shift, the organisation says, Europe must take advantage of the decentralisation trend through new IoT and edge computing capabilities.
The continent has the opportunity to make use of its well-established communities in the physical, industrial world and in the digital world to bring the best of both to Europe’s next generation of IoT and edge computing infrastructure. NGIoT believes that edge computing will have a radical impact on how sensing, evaluation and control of our environments are achieved. The organisation believes that edge capabilities will be central to the adoption of cloud, artificial intelligence (AI), energy aggregation, manufacturing, precision farming, autonomous vehicles and many other vertical activities that are part of a wave of innovation that will dramatically improve the lives of European populations.
That vision remains some way off with mass market IoT only now truly arriving in Europe which continues to be one of the leading regions in terms of adoption in the world. Europe’s position as a leading IoT region will endure thanks to committed investment by enterprises which IDC’s ‘Worldwide Semiannual Internet of Things Spending Guide’ estimates will total US$208 billion in 2022 in Europe. This growth will continue at a double-digit rate until at least 2026 and comes in spite of the current challenges of the Russia-Ukraine War, the aftermath of the pandemic and the economic challenges affecting the continent. IDC says increased spending will continue in areas in which improving business performance is essential such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail and infrastructure.
“During the pandemic, many organisations refocused their technology investment plans, aiming for a technology stack to support innovation, efficiency and performance, even in challenging situations – such as the Russia-Ukraine War – with IoT and automation at the core,” says Alexandra Rotaru, a research analyst for Data and Analytics, Europe, at IDC. “With organisations seeking to improve productivity, reduce costs, better orchestrate resources and assets, and enhance customer experience, IoT will remain on the agenda for many technology leaders in the years to come.”
In fact, the firm says the largest share of spending in Europe will be in the manufacturing and resources sector, directed at predictive maintenance and production asset management in which IoT is used to enhance manufacturing organisations’ tracking, monitoring and maintenance of industrial devices.
The fastest rate of adoption according to IDC will be in electric vehicle (EV) charging in Europe, driven by the expansion of commercial EV charging stations across the continent, with IoT enabling real-time availability and reservation scheduling, charge notifications, automated billing, and value-added services, as well as offering marketing opportunities.
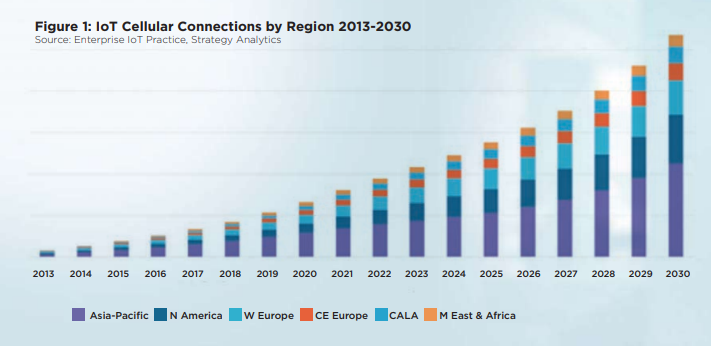
Europe’s position as an early adopter of IoT is borne out by Transforma Insights’ ‘Global IoT Forecast Report 2021-2030’ which projects that Europe will account for 20% of the value of the IoT market in 2030, behind China and North America with 30% and 20% respectively. The report paints a picture of a maturing IoT industry with 11.3 billion active IoT devices at the end of 2021 which will grow to 29.4 billion in 2030.
A new report from IoT market research firm Berg Insight also sees active subscriptions increasing, reporting that the global number of cellular IoT subscribers increased by 22% during 2021 to reach 2.1 billion. The major regional markets China, Western Europe and North America, grew similarly during the year as the world recovered from the COVID 19 pandemic.
The top ten mobile operators reported a combined active base of 1.8 billion cellular IoT connections at the end of 2021, accounting for 86% of total connections. China Mobile is the world’s largest provider of cellular IoT connectivity services with an estimated 801 million cellular IoT connections. China Unicom and China Telecom ranked second and third with 300 million and 297 million connections respectively.
Vodafone ranked first among the western operators and fourth overall with 142 million connections, followed by AT&T with 95 million in fifth place. Deutsche Telekom and Verizon had in the range of 45–55 million cellular IoT connections each, when counting T-Mobile USA’s customers as part of Deutsche Telekom’s IoT subscriber base. Telefónica, KDDI and Orange were the last players in the top ten with about 31 million, 23 million and 20 million connections respectively.
These huge numbers don’t mean massive revenues for operators and IoT connections still represent only a small share of their business. IoT connectivity services account for only around 1% of total revenues for most operator groups. Berg Insight’s analysis of the IoT business KPIs released by mobile operators in different parts of the world suggests that global IoT connectivity revenues increased by around 15% during 2020, while the monthly average revenue per user (ARPU) dropped by 2% to €0.38.
Europe’s position behind China and North America is expected to continue to at least 2030, reports Strategy Analytics pointing out that while there will be regional differences between the cellular technologies adopted, substantial growth will be seen in all markets. 5G will start to gain traction, the firm says: while 4G will continue to dominate overall, driven by 2G replacements, especially in China, but also elsewhere. 3G will retire with most connections moving to 4G and the firm expects 5G to total 47% of connections by 2030, while 4G will remain the dominant technology at 49%.

“The adoption of 5G will likely happen in different stages, with extended mobile broadband (eMBB) reaching mass adoption first, ultra-reliable low latency communications (uRLLC) gaining traction soon afterward, and massive machine-type communication (mMTC) showing the longest tail,” says Gina Luk, the director of Enterprise Research at Strategy Analytics. “Adoption will be determined by the availability of 5G chipsets, the speed and coverage of 5G networks, and as well as the evolution of regulations. The engine for driving 5G forward for fast growth and rapid adoption is its radio access technology, referred to as new radio (NR). One recent example is NR support for reduced capability (RedCap) devices which can facilitate the expansion of the NR device ecosystem to cater to use cases include wearables such as sensors and video surveillance, as these are not yet best served by the current NR specifications.”
Projections can only go so far, especially when covering a large and diverse region such as Europe. What is clear is that Europe has recovered relatively quickly from the COVID 19 pandemic and increasing spending, although hampered by the supply chain crisis. IoT Analytics says that technology budgets differed widely from region to region going into 2022 and are still correlated to the pandemic’s impact. North America and Europe have increased IoT technology spending while in APAC and the rest of the world there is heightened caution with regard to innovation and technology investments.
Security becomes essential spending
The growth in number of IoT connections is creating an expanded threat surface that exposes organisations to new vulnerabilities. IoT security spending is therefore becoming mandatory and regulations are being put in place to mandate minimum standards and protections for users’ data.
Bloomberg has reported that the regulatory landscape for IoT is evolving rapidly as governments seek to mitigate risks. The governments of various countries have put in place regulations and these will drive investment in IoT security. Examples include:
In 2021, the UK government introduced the Product Security and Telecommunications Infrastructure (PSTI) Bill to secure consumers from IoT threats and protect IoT devices. In 2020, the US government passed a new IoT cybersecurity law, the NIST Internet of Things Cybersecurity Improvement Act, to increase cybersecurity for IoT devices. Also, in 2020, the Australian government released a voluntary code of practice to improve Internet of Things (IoT) security in Australia, including smart devices. Finally, the European Technical Standards Institute (ETSI) has released ETSI EN 303 645, a standard for cybersecurity in the Internet of Things that establishes a security baseline for internet-connected consumer products.
With these and other planned regulation, the regulatory framework for IoT security is becoming progressively more stringent as governments are considering connected device-associated issues of enterprises as a serious risk. Tightening IoT security regulations are expected to drive the growth of the IoT security market over the coming years.
This year, the software segment is expected to account for the larger share of the IoT security market. The large share of this segment is attributed to the rising investments in R&D, increasing focus on software-centric security capabilities, and increasing data and security breaches. However, the services segment is expected to grow at a higher CAGR during the forecast period because of growing demand for IoT security services among small and medium enterprises and the increased need to improve business processes and optimise business infrastructure.
Based on security type, the IoT security market is segmented into network security, endpoint security, application security, cloud security and other security types. This year, Bloomberg predicts that the network security segment will account for the largest share of the IoT security market. However, the cloud security segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period because of greater need to secure workload on cloud and the growing trend of bring your own device (BYOD) and working from home.
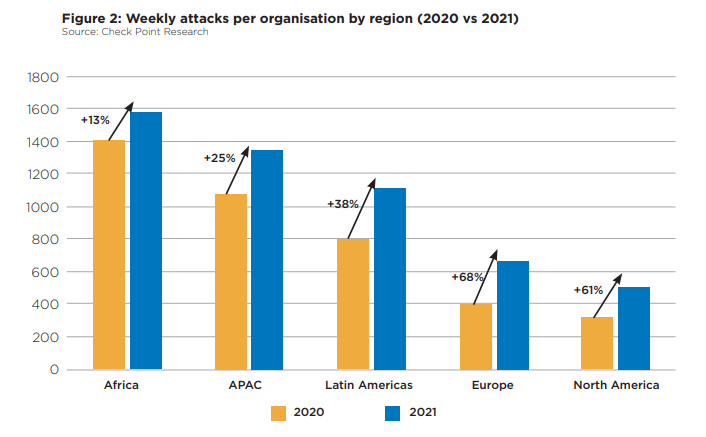
Regional differences are also apparent here with different regions experiencing various volumes of attacks. According to Check Point Research, Africa experienced the highest volume of attacks in 2021, with an average of 1,582 weekly attacks per organisation. This represents a 13% increase from 2020.
This was followed by APAC, which has an average of 1,353 weekly attacks per organisation (a 25% increase); Latin America, with 1,118 attacks weekly (a 38% increase); Europe, with 670 attacks weekly (a 68% increase); and North America, with an average of 503 weekly attacks per organisation (a 61% increase).
In spite of still recovering from the impacts of the pandemic and suffering the economic and material consequences of the Russia-Ukraine War, Europe continues to be an innovative region, open to adopting new technologies and investing in the infrastructure that is needed to enable them to operate efficiently. In IoT terms, this translates to sustained investment for a better future with the region’s commitment to EV charging a clear indicator of continued spending. IoT is just one aspect of the region’s digital future but with ample connectivity infrastructure, appropriate laws that protect users and IoT service providers and the R&D base to turn ideas into reality, European IoT looks to be set for massive growth inline with massive IoT.
Comment on this article below or via Twitter: @IoTNow_










